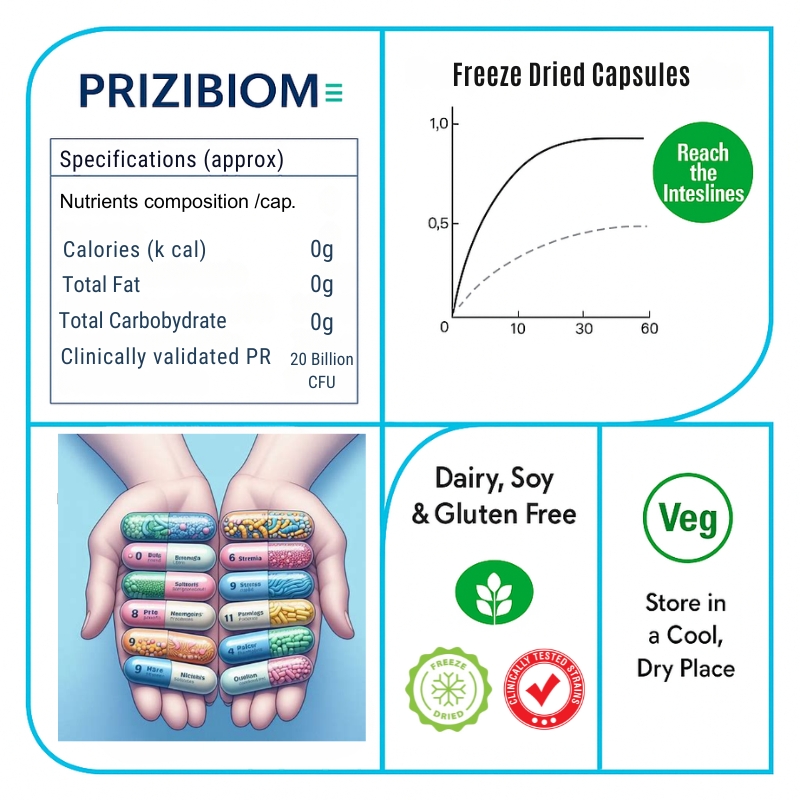
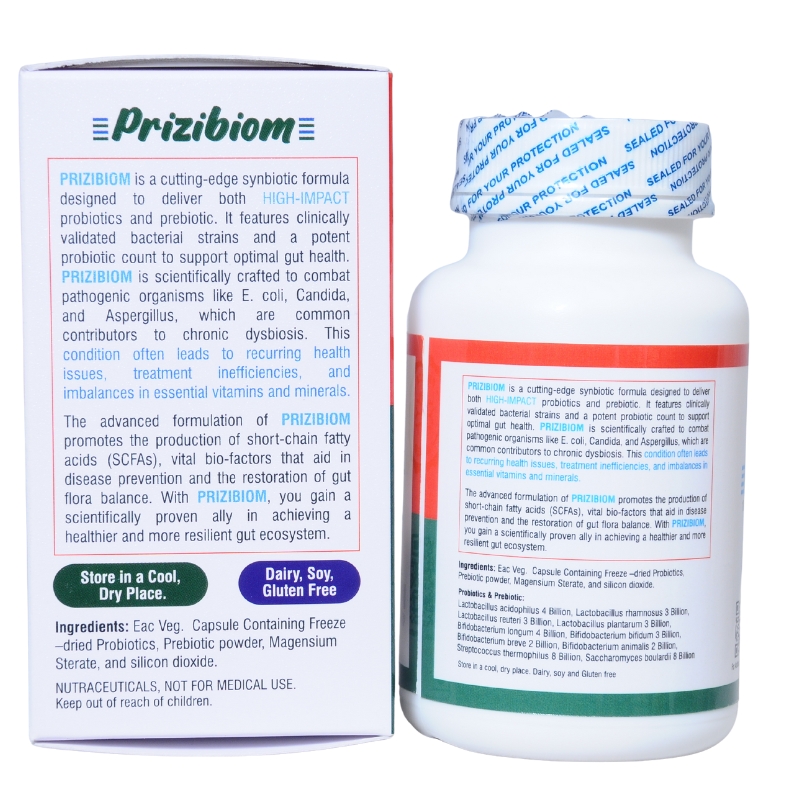
Advantage Prizibiom
Prizibiom works through multiple complementary pathways—enhancing gut barrier integrity, suppressing inflammation, producing short-chain fatty acids, and improving microbial diversity. This leads to better digestion, reduced bloating, and improved bowel regularity, while also boosting insulin sensitivity, vitamin synthesis, and nutrient absorption. Additionally, Prizibiom helps prevent overgrowth of harmful bacteria and yeast, supports immune function, and plays a supportive role in managing PCOS, IBS/IBD, chronic allergies, SIBO, and metabolic conditions. Its vegetarian capsules are easy to use (1–2 per day), making it a safe.
Recommended Usage
Supports the restoration of healthy microbial balance after prolonged antibiotic or medical treatments, helping prevent intestinal bacterial overgrowth and candida/fungal proliferation. Prizibiom enhances gut barrier integrity, reduces local and systemic inflammation, and improves short-chain fatty acid production, which is vital in managing metabolic diseases and PCOS. Its influence on the gut-brain axis offers supportive benefits in individuals facing prolonged depressive symptoms, while its immune-modulatory effects make it useful in chronic allergic conditions like asthma, eczema, and psoriasis. This multi-targeted approach makes Prizibiom a safe and effective adjunct for gastrointestinal, metabolic, immune, and neuropsychological health.
Recommended Dose
1 capsule daily for 10 days and based on tolerance dose can be increased to twice daily or as recommended by the healthcare expert.
Evidences Supporting High CFU Probiotics
1. Probiotic–Fiber Blend in Obesity (2025)
Journal: Obesity & Metabolism Research
Key findings:
-
In a 12-week RCT, obese adults taking a synbiotic (~30B CFU + prebiotic) achieved significant reductions:
-
Body weight (−12%)
-
BMI (−12%)
-
Waist/hip circumference (∼9.6%)
-
Triglycerides (−26%)
-
-
Also observed: increased HDL and improved digestion.
Conclusion: High-CFU synbiotics with fiber effectively support weight and metabolic health.
PubMed: PMC10120130
2. Metabolic Syndrome Systematic Review (2025)
Journal: International Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Key findings:
-
Meta-analysis of 24 RCTs (n=1186) showed probiotics/synbiotics significantly reduced:
-
Weight (−0.79 kg)
-
Waist circumference (−1.04 cm)
-
Triglycerides, total cholesterol, fasting glucose, insulin
-
Raised HDL
-
Conclusion: High-dose microbiome interventions safely improve metabolic markers in MetS.
Links:
reddit.com + pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
3. Prediabetes Synbiotic Trial (2018, follow‑up synthesis)
Journal: Diabetes India
Key findings:
-
In 120 prediabetics, synbiotic (~25B CFU) decreased:
-
Hyperglycemia prevalence (p=0.005)
-
Hypertension (p=0.04)
-
Low HDL (p=0.02) compared to controls .
-
Conclusion: High-potency synbiotics aid metabolic risk reduction before diabetes onset.
4. Pilot Synbiotic in Functional Diarrhea (2024)
Journal: Nutrients
Key findings:
-
Eight-week synbiotic (~25B CFU + FOS) increased stool solidity, reduced calprotectin, and improved patient satisfaction in adults, raising Lactobacillales abundance.
Conclusion: High-dose synbiotics enhance gut barrier function and reduce inflammation in functional diarrhea.
5. IBS‑D RCT with Multi-Strain Synbiotic (2020)
Journal: Journal of Gastrointestinal Disorders
Key findings:
-
Eight-week multi-strain synbiotic (~25B CFU) significantly improved:
-
IBS-SSS
-
Flatulence
-
Pain
-
Bowel habits
-
Overall symptom relief (p<0.05)
-
Conclusion: High-CFU synbiotics effectively reduce symptoms in IBS-D.
6. Schizophrenia‑Related Metabolic Syndrome RCT (2024)
Journal: Psychiatry & Metabolic Health
Key findings:
-
Over 8 weeks, ~30B CFU synbiotic reduced:
-
Waist circumference
-
HbA1c
-
LDL cholesterol
-
Prevented BMI rise in antipsychotic-treated patients
-
Conclusion: High-CFU synbiotics counteract metabolic side effects in schizophrenia.
7. Obesity Synbiotic Trial (MN‑Gup) (2024)
Journal: Clinical Obesity Research
Key findings:
-
Twelve-week synbiotic (1×10¹¹ CFU MN-Gup + prebiotics) significantly reduced:
-
Body fat
-
Waist circumference
-
LDL-C
-
-
Also: Raised satiety hormones and beneficial microbes.
Conclusion: Large-dose synbiotics positively modulate body composition and metabolic hormones.
8. PCOS Synbiotic Review (2024)
Journal: Nutrients
Key findings:
-
Systematic review: synbiotics (≥25B CFU/day) improved:
-
HOMA‑IR
-
Fasting glucose/insulin
-
LDL/triglycerides
-
Increased SHBG and reduced testosterone more than probiotics/prebiotics alone.
-
Conclusion: High-CFU synbiotics beneficially influence metabolic and hormonal markers in PCOS.
9. IBS Systematic Review & Meta-analysis (2023)
Journal: PMCID
Key findings:
-
Review of 72 RCTs found probiotics ≥10⁹ CFU/day significantly improved IBS symptoms (SMD –0.55) and abdominal pain (SMD –0.89).
Conclusion: High-dose probiotic formulas (≥25B CFU) are effective for IBS relief.
10. Female IBS RCT (2024)
Journal: Neurogastroenterology & Motility
Key findings:
-
A double-blind trial (women 18–40) showed that an 8-week ~25B CFU probiotic reduced IBS-SSS by ≥80 points with high statistical significance.
Conclusion: High-potency probiotics offer clinically meaningful IBS symptom relief.
11. NAFLD Synbiotic Yogurt (2018, referenced in recent meta-analyses)
Journal: Journal of Nutrition
Key findings:
-
Daily high-dose synbiotic yogurt reduced liver steatosis on imaging and improved liver enzymes.
Conclusion: High-CFU synbiotic yogurt is a safe adjunct in NAFLD management.
12. Gestational Diabetes Prevention Meta‑analysis (2023)
Journal: Annals of Translational Medicine
Key findings:
-
≥10B CFU probiotics for ≥8 weeks lowered fasting glucose, insulin, and HOMA-IR in pregnant women.
Conclusion: High-potency probiotics reduce GDM risk and improve glycemic control.
13. Gut-Brain Axis: Synbiotic in Depression (Hemodialysis) (2021)
Journal: Nutritional Neuroscience
Key findings:
-
Synbiotics (~25B CFU) improved serum BDNF levels and reduced depression/anxiety scores in hemodialysis patients over 8 weeks.
Conclusion: High-dose synbiotics support neuropsychiatric health via gut-brain axis modulation.
14. Type 2 Diabetes Glucose Control Meta‑analysis (2023)
Journal: Jr of Diabetes Care
Key findings:
-
39 RCTs (n=3517) showed probiotics/synbiotics significantly lowered:
-
Fasting glucose (SMD –0.30)
-
HbA1c (SMD –0.59)
-
HOMA-IR (SMD –0.68)
-
Conclusion: High-CFU microbiome therapies effectively improve glycemic control in diabetes.
15. High‑Dose Synbiotic in Active Crohn’s Disease (Fujimori et al., 2007)
Journal: Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Key findings:
-
In a 13-month, open-label study of 10 patients with active Crohn’s disease unresponsive to standard therapy, participants received a daily synbiotic therapy — probiotics (~45 billion CFU/day) comprising Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, plus psyllium prebiotic.
-
Significant reductions in Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (CDAI) from 255 to 136 (p = 0.009) and IOIBD score from 3.5 to 2.1 (p = 0.03).
-
Clinically, 6 patients achieved complete remission, 1 had partial response, and 3 did not respond.
-
Notably, 2 patients discontinued corticosteroids and 4 reduced their steroid dose. No adverse events were reported.
Conclusion: High‑dose probiotic/prebiotic therapy (≈45 B CFU + psyllium) can be safely and effectively used to induce remission in active Crohn’s disease, reducing disease activity and steroid dependence.
Relevance to Prizibiom
These rigorous studies collectively reinforce that daily administration of ≥25–30 billion CFU probiotic/prebiotic blends, especially when combined with prebiotics, delivers meaningful, clinically significant outcomes in:
-
Metabolic Health: weight, BMI, waist circumference, lipid/glucose markers (Obesity, MetS, T2D, PCOS)
-
Gut Disorders: IBS-D/FDr symptom relief, diarrheal control, calprotectin reduction
-
Liver and GI Protection: NAFLD improvement, gut barrier function
-
Neuropsychological Impact: mood improvement via gut–brain axis modulation
-
Endocrine/Immunological Conditions: PCOS, gestational diabetes risk reduction
This body of evidence strongly supports the design of Prizibiom’s 40B CFU, 10‑strain synbiotic formulation, reaffirming its dose rationale, multi-strain synergy, and broad-spectrum therapeutic potential.




dr Sukumar –
though initially i had bit of GI disturbances, say for 2-3 days, thereafter the product worked very well for me. Now i taking 2 capsules in divided dose and almost got rid of my ibs issues.
See –
just received Prizibiome and i think it will very well because it is only probiotic that s giving 4 specc. of lactobacillus in the same capsule, that too good concentration.