Introduction: Why We Need to Rethink Iron Therapy
Iron deficiency anemia is still one of the most common nutritional issues around the globe, impacting pregnant women, new mothers, teens, athletes, and those dealing with chronic metabolic or inflammatory conditions. Even though oral iron supplements are widely available, the real-world results often fall short due to issues like poor tolerability, low adherence, incomplete treatment, and functional non-response.
The challenge isn’t the lack of iron options; it’s the gap between iron chemistry, how our gastrointestinal system works, inflammatory responses, and how well patients stick to their treatment plans. Traditional iron salts frequently provide iron in a way that the gut struggles to handle or that the body can’t use effectively.
This has sparked increasing interest in liposomal iron systems, especially liposomal ferric pyrophosphate paired with liposomal lactoferrin and Vitamin B12. This approach aligns iron delivery with how our bodies naturally metabolize iron, rather than bombarding the gastrointestinal tract. Precifer Capsules are crafted with this physiological principle in mind.
Why Conventional Oral Iron Preparations Often Fall Short
The iron supplements we often see prescribed—like ferrous ascorbate, ammonium ferric citrate, carbonyl iron, iron polymaltose, and heme iron polypeptide—have a common drawback: they tend to release free iron ions right in the gastrointestinal tract.
This can lead to:
- Gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, stomach pain, constipation, or diarrhea
- Oxidative stress in the gut
- Changes in gut microbiota
- High rates of discontinuation, particularly during pregnancy and adolescence
In everyday practice, it’s not uncommon for 30–70% of patients to stop taking conventional iron therapy too soon, which can result in incomplete treatment of anemia and a need to switch to parenteral iron—even in situations where oral treatment would have been enough.
Liposomal Ferric Pyrophosphate: A Smart Way to Deliver Iron
Ferric pyrophosphate is a stable, non-ionic form of iron that doesn’t break down into free iron ions in the gut. But when it’s wrapped up in a liposomal phospholipid bilayer, everything changes about how it gets delivered.
So, what’s great about liposomal ferric pyrophosphate?
- It’s shielded from the harshness of gastric acid
- It doesn’t create free radicals in the gut
- It avoids irritating the mucosal lining
- It allows for a steady absorption in the intestines
Unlike ferrous salts, which rely heavily on stomach acidity and specific transporters, liposomal iron takes advantage of different absorption routes. This means it can deliver iron more reliably, even when the gut isn’t in the best shape.
Why the Combination Must Be Liposomal Iron + Liposomal Lactoferrin
Let’s talk about why combining liposomal iron with liposomal lactoferrin is so important. It’s essential to understand that the real benefits come from pairing liposomal ferric pyrophosphate with liposomal lactoferrin, rather than using regular lactoferrin.
Lactoferrin is a delicate iron-binding glycoprotein that gets broken down quickly by stomach acid and digestive enzymes when taken in its standard oral form. However, when it’s encapsulated in liposomes, it maintains its structure and keeps its biological activity intact as it travels through the gastrointestinal tract.
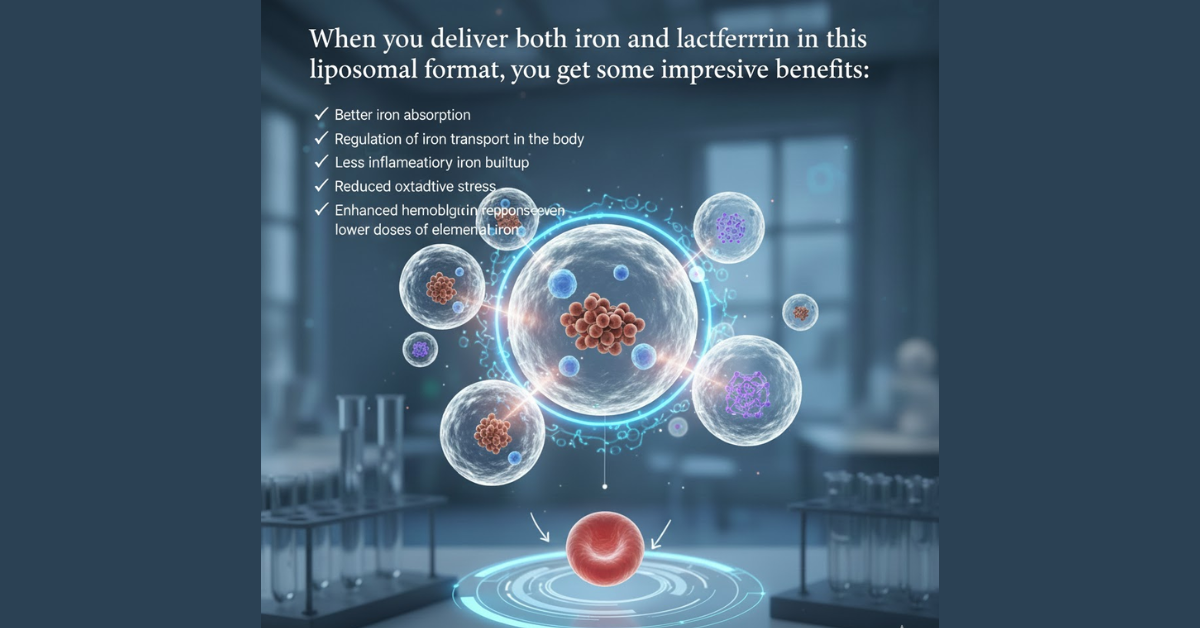
When you deliver both iron and lactoferrin in this liposomal format, you get some impressive benefits:
- Better iron absorption
- Regulation of iron transport in the body
- Less inflammatory iron buildup
- Reduced oxidative stress
- Enhanced hemoglobin response even with lower doses of elemental iron
The Central Role of Liposomal Lactoferrin in Iron Regulation
Liposomal lactoferrin serves two important functions. First, it acts as a natural iron transporter, helping to deliver iron to the cells that need it most, like erythroid precursors. Second, it plays a role in reducing inflammation, which can help lower the signals that cause the body to hold onto iron. By managing how iron moves around instead of just boosting the amount of iron in the gut, liposomal lactoferrin enhances how effectively the body uses iron—particularly in patients who have iron available but can’t use it properly.
Liposomal lactoferrin serves two important functions. First, it acts as a natural iron transporter, helping to deliver iron to the cells that need it most, like erythroid precursors. Second, it plays a role in reducing inflammation, which can help lower the signals that cause the body to hold onto iron. By managing how iron moves around instead of just boosting the amount of iron in the gut, liposomal lactoferrin enhances how effectively the body uses iron—particularly in patients who have iron available but can’t use it properly.
This dual-liposomal strategy mimics the body’s natural way of handling iron, which is why people often experience better tolerance and more consistent results with Precifer Capsules.
Anemia of Inflammation: Why “More Iron” Is Often the Wrong Answer
In clinical practice, a significant amount of anemia we see is actually anemia of inflammation (AI) or a mix of different types, rather than just pure iron deficiency anemia.
When inflammation kicks in, it raises levels of hepcidin, a hormone produced by the liver that hinders the absorption of iron in the intestines and keeps iron locked away in macrophages. Because of this, traditional oral iron treatments often lead to:
- A minimal increase in hemoglobin levels
- More gastrointestinal side effects
- Higher oxidative stress
Some common situations where this occurs include:
- Gestational diabetes and high blood pressure during pregnancy
- Pre-eclampsia
- Inflammatory issues after childbirth
- Rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases
- Chronic metabolic inflammation and diabetes
- Anemia linked to obesity
In these cases, simply upping the iron dosage rarely leads to better results.
Why Liposomal Lactoferrin Is Especially Valuable in Inflammatory Anemia
Liposomal lactoferrin plays a crucial role in tackling the underlying issues of inflammatory anemia by:
- Reducing inflammatory signals
- Modulating hepcidin activity
- Helping to mobilize iron from storage
- Enhancing the utilization of erythropoietin
What makes liposomal lactoferrin stand out is its ability to stay biologically active even after digestion, making it a powerful ally in restoring iron balance for patients who struggle with traditional iron treatments. Dr. Raghav Deshpande describes liposomal lactoferrin as an iron traffic controller, ensuring that iron makes its way to the bone marrow instead of getting trapped during periods of chronic inflammation.
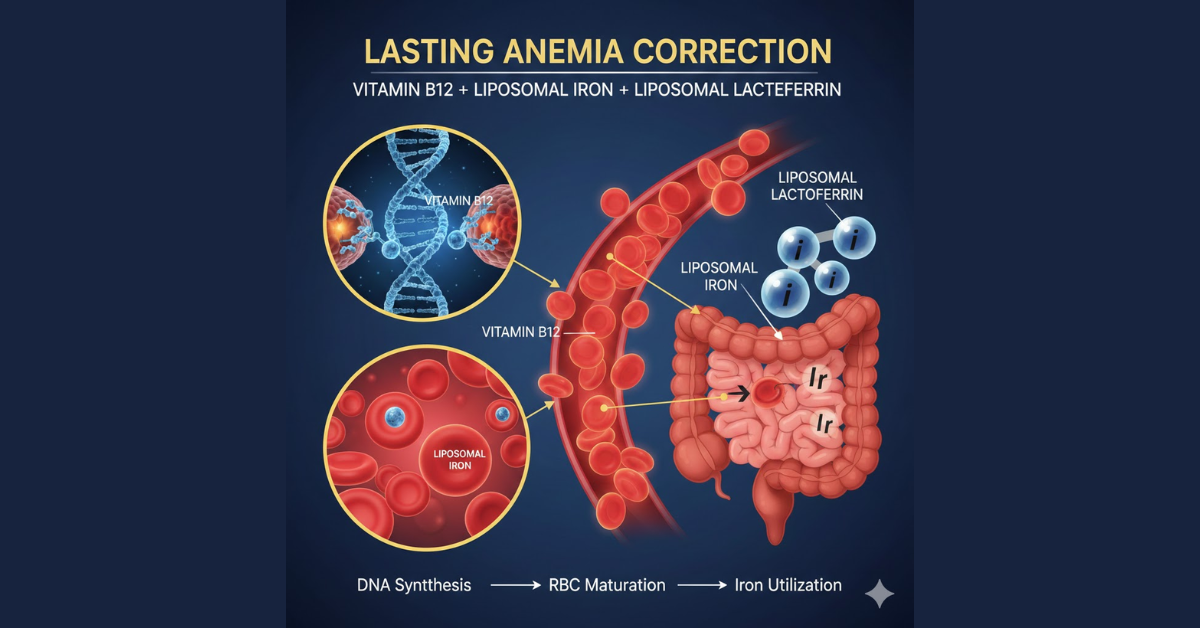
Vitamin B12: Completing the Erythropoietic Equation
Iron therapy on its own might not be enough if the body’s ability to produce red blood cells is hampered by a lack of functional Vitamin B12. This deficiency is often found in vegetarians, adolescents, postpartum women, and older adults.
Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in:
- DNA synthesis
- Maturation of red blood cells
- Efficient use of absorbed iron
By incorporating Vitamin B12 with liposomal iron and liposomal lactoferrin, you can achieve a thorough and lasting correction of anemia, rather than just a temporary boost in hemoglobin levels.
Comparison of Oral Iron Forms in Clinical Practice
Iron Form | Approx. Absorption | GI Side Effects | Treatment Discontinuation |
Ferrous ascorbate | 50-60% | Moderate | Moderate |
Ammonium ferric citrate | 8–15% | Moderate–High | Moderate |
Carbonyl iron | 5–10% | Moderate | Moderate |
Iron polymaltose | 10–15% | Moderate | Moderate |
Heme iron | 15–25% | Low | Moderate (cost-related) |
Liposomal ferric pyrophosphate + liposomal lactoferrin | >30% functional uptake | Very low | Low |
Why Concentration and Liposomal Integrity Matter
Not every “liposomal iron” product actually provides the clinical benefits you might expect. Here are some common issues that can arise with these formulations:
- A low percentage of liposomal iron
- Inefficient encapsulation
- Tablet compression that damages the liposomal structure
- Poor stability in real-world conditions
On the other hand, capsule-based systems like Precifer are designed to maintain liposomal integrity. They deliver clinically significant amounts of liposomal ferric pyrophosphate and liposomal lactoferrin, which helps ensure consistent absorption and positive outcomes.
Discover the real-world benefits of Precifer from clinicians working with various populations. Here’s what they’re seeing:
- For pregnancy-related anemia, patients are experiencing better tolerance and sticking to their treatment plans.
- After childbirth, women are recovering more quickly without the usual gastrointestinal issues.
- Adolescents, including students and athletes, are showing improved adherence to their iron regimens.
- Athletes are correcting their iron levels without any negative impact on gut health.
Dr. Shirish Patwardhan emphasizes that the combination of liposomal iron and liposomal lactoferrin marks a major step forward in managing maternal anemia, especially during inflammatory pregnancy conditions.
Dr. Pramila Gupta has observed that peri- and post-menopausal women are enjoying higher energy levels and more stable hemoglobin levels.
From a wellness standpoint, Dr. Charulatha points out that adolescents and women moving away from traditional iron supplements are experiencing much better gut tolerance and compliance.
Practical Flow: Anemia Management Across Populations
Step 1: Identify anemia type
CBC, ferritin, CRP, Vitamin B12
Step 2: Assess inflammatory load
Pregnancy complications, autoimmune disease, metabolic syndrome
Step 3: Choose intervention
Mild anemia → Iron-rich diet + Precifer
Moderate anemia → Precifer Capsules
Inflammatory anemia → Liposomal iron + liposomal lactoferrin
Step 4: Review at 4–6 weeks
Hb rise ≥1 g/dL → continue
Suboptimal response → address inflammation, reassess cofactors
Step 5: Reserve IV iron
Only for true refractory cases
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Why liposomal iron over ferrous salts?
Better absorption and tolerance. - Is ferric pyrophosphate effective?
Yes, especially when liposomalized. - Does liposomal iron cause constipation?
Rarely. - Is it safe in pregnancy?
Yes, widely used. - Why liposomal lactoferrin?
It regulates iron and reduces inflammation. - Can it help anemia of inflammation?
Yes, significantly. - Does it replace IV iron?
In many mild–moderate cases. - Is Vitamin B12 essential?
Yes, for full erythropoiesis. - Suitable for adolescents?
Yes. - Suitable for athletes?
Yes. - Does it disturb gut microbiota?
Much less than ferrous salts. - Can it be taken empty stomach?
Yes. - Is capsule better than tablet?
Yes, preserves liposomes. - How soon Hb rises?
3–4 weeks. - Is it cost-effective?
Yes, over full treatment. - Suitable for elderly?
Very well tolerated. - Does it stain teeth?
No. - Can diabetics take it?
Yes. - Is it better than polymaltose?
Clinically, yes. - When to escalate therapy?
Only after true oral failure
Final Take-Home Message
Iron therapy must move beyond elemental dosing toward physiology-aligned delivery.
The combination of liposomal ferric pyrophosphate, liposomal lactoferrin, and Vitamin B12, as formulated in Precifer Capsules, addresses absorption, regulation, inflammation, and compliance simultaneously.
This approach delivers predictable, sustained correction of anemia across pregnancy, postpartum, adolescence, athletes, and inflammatory conditions—marking a meaningful shift in modern anemia management.