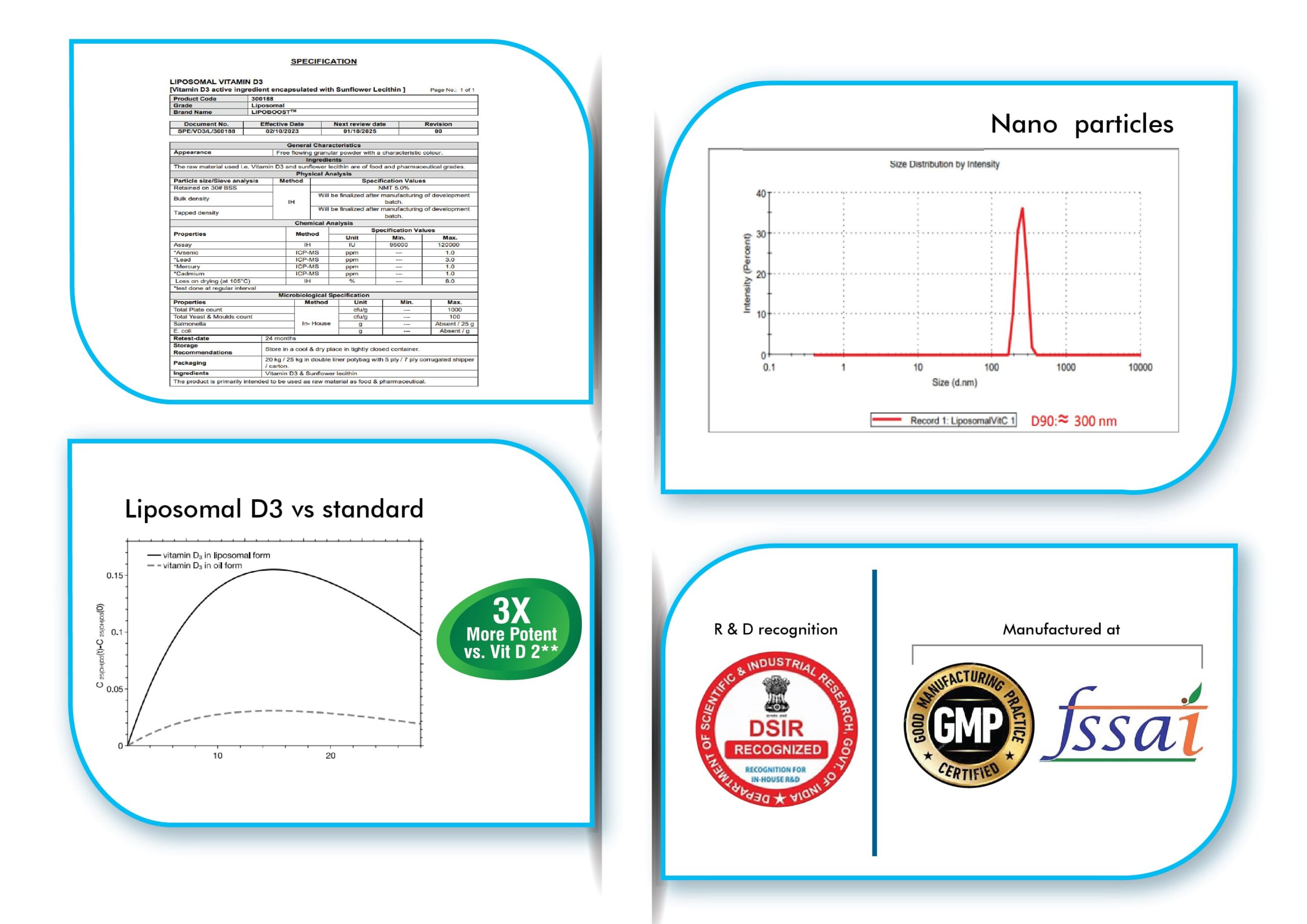
Despite the widespread availability of Vitamin D3 and D2 formulations, Vitamin D3 deficiency continues to rise and remains a major issue. As a fat-soluble vitamin, conventional dosage forms like nano shots, capsules, tablets, gummies, and mouth-dissolving films have limited absorption, resulting in partial or sometimes incomplete efficacy. Liposomal delivery utilizes liposomes to enhance nutrient absorption, protecting Vitamin D3 from degradation. This method improves solubility and bioavailability, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract for direct absorption. Liposomes facilitate the transport of Vitamin D3 into cells, ensuring optimal delivery. By utilizing liposomal delivery, liposomal Vitamin D3 provides a more efficient way to increase Vitamin D levels and support overall health. With liposomal technology, the benefits of Vitamin D3 can be maximized, offering a convenient and effective solution for individuals seeking to optimize their Vitamin D status. Thus, Precimax Liposomal Vitamin D3 emerges as the preferred choice for a daily dose of Vitamin D3 for all ages.
Recommended Use
- Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis
- Cardiovascular Health
- Diabetes Management
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Migraines
- Support in Major Depression /Bi-polar disorders
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
- Asthma
- Chronic Fatigue
- Muscle Functions
- Hypertension
- Hyperlipidemia
- Cancer Prevention
Recommended Dosage
1 -2 capsules daily, taken with breakfast or lunch, or as recommended by healthcare experts.
Evidence
Latest Scientific Studies on Liposomal Vitamin D3
Bioavailability by design — Vitamin D3 liposomal delivery vehicles; Nanomedicine 2022
Key Findings
Because of high hydrophobicity, its absorption and subsequent redistribution throughout the body are inherently dependent on the accompanying lipids and/or proteins. The effective oral vitamin D3 formulation should ensure penetration of the mucus layer followed by internalization by competent cells. Studies have shown that vitamin D3 molecules cannot leave the hydrophobic environment, indicating that their absorption is predominantly driven by the digestion of the delivery vehicle. In the clinical experiment, liposomal vitamin D3 was compared to the oily formulation. The results obtained show that liposomal vitamin D3 causes a rapid increase in the plasma concentration of calcidiol.
Click below to know more
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8957331/
Relative Efficacy of Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3 in Improving Vitamin D Status: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis; Nutrients 2021
Key Findings
Compared to ergocalciferol (Vitamin d3), cholecalciferol (Vitamin d2) intervention was more efficacious in improving vitamin D status (serum levels of total 25(OH)D and 25(OH)D3) and regulating PTH levels, irrespective of the participant demographics, dosage and vehicle of supplementation.
Click below to know more
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103328
Novel Approach for the Approximation of Vitamin D3; Pharmaceutics 2023
Key Findings
The changing environment and modified lifestyles have meant that many vitamins and
minerals are deficient in a significant portion of the human population. Therefore, supplementation is a viable nutritional approach, which helps to maintain health and well-being. The supplementation efficiency of a highly hydrophobic compound such as cholecalciferol (logP > 7) depends predominantly on the formulation. To overcome difficulties associated with the evaluation of pharmacokinetics of cholecalciferol, a method based on the short time absorption data in the clinical study and physiologically based mathematical modeling is proposed. The method was used to compare pharmacokinetics of liposomal and oily formulations of vitamin D3. The liposomal formulation was more effective in elevating calcidiol concentration in serum. The determined AUC value for liposomal vitamin D3 formulation was four times bigger than that for the oily formulation.
Click below to know more
https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030783
Comparison of the Effect of Daily Versus Bolus Dose Maternal Vitamin D3 Supplementation on the 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 Ratio; Jr Bone 2018
Key findings
Daily vitamin D3 supplementation may provide more predictable effects on vitamin D status due to the greater stability of the 24,25(OH)2D3/25(OH)D3 ratio compared with bolus dosing.
Click below to know more
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29486367/
Vitamin D supplementation: better daily or by bolus?; University of Verona Publication 2021
Key findings
Daily doses could therefore have the distinct advantage of maintaining stably high levels of vitamin D in the circulation by constantly stimulating immune T cells. On the other hand, bolus administrations are rapidly converted to 25(OH)D with circulating D2 and D3 levels dropping rather quickly [17]. Figure 2 shows the hypothesized different effect on extra-skeletal effects of vitamin D bolus compared to daily administration. In conclusion, we believe that there is now pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and clinical evidence to justify the preferential choice of the daily supplementation strategy over the bolus strategy.
Click below to know more
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29486367/
Vitamin D: Bolus Is Bogus—A Narrative Review; Jr of Bone & Mineral Research 2021
Key findings
In this review we summarized and discussed growing evidence that large bolus dosing of vitamin D may have minimal benefit, or even be counterproductive, whereas small to moderate daily dosing in individuals at risk of deficiency is beneficial. This applied to outcomes of rickets, musculoskeletal health (falls and fractures), as well as respiratory infections and cancer mortality, and possibly weekly dosing for calcifediol with regard to COVID-19. However, as discussed above in the section on falls and fractures, the benefits of daily dosing have been absent in several studies among vitamin D–replete adults and those not at risk for the outcomes of interest (ie, falls and factures(73, 74)), and although this needs further study, we cannot exclude that higher daily doses may also trigger countervailing factors.(24)
Click below to know more
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/jbm4.10567
Mayo Clinic Recommendation ;2024
The Endocrine Society, along with the Canadian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism and the National Osteoporosis Foundation, published a clinical practice guideline in 2011 titled “Evaluation, Treatment and Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency.” The committee recommended screening of only those individuals who are at high risk for vitamin D deficiency, including patients with osteoporosis or a malabsorption syndrome, as well as black and Hispanic individuals, obese persons (BMI >30 kg/m2), and those with several other medical conditions.
The daily maintenance dose of vitamin D varies by age, but most children and adults generally require 600-2000 IU of vitamin D daily. For vitamin D-deficient children and adults, higher doses of vitamin D given either daily or weekly are recommended, followed by an increase in the daily dose of vitamin D. [2]



Sumukh Sing –
i took Liposomal Vitamin D, twice daily for 3 months and got my vitamin d3 level getting back to normal. did not experience any side effects too!
i think it is a better vitamin D3 option………….
Sumukh Sing –
i took Liposomal Vitamin D, twice daily for 3 months and got my vitamin d3 level getting back to normal. did not experience any side effects too!
i think it is a better vitamin D3 option………….
Sumukh Sing –
i found Liposomal vitamin d3 of precimax a better option because, with twice daily for 3 months and got my vitamin d3 level getting back to normal.
moreover, i did not experience any side effects too!