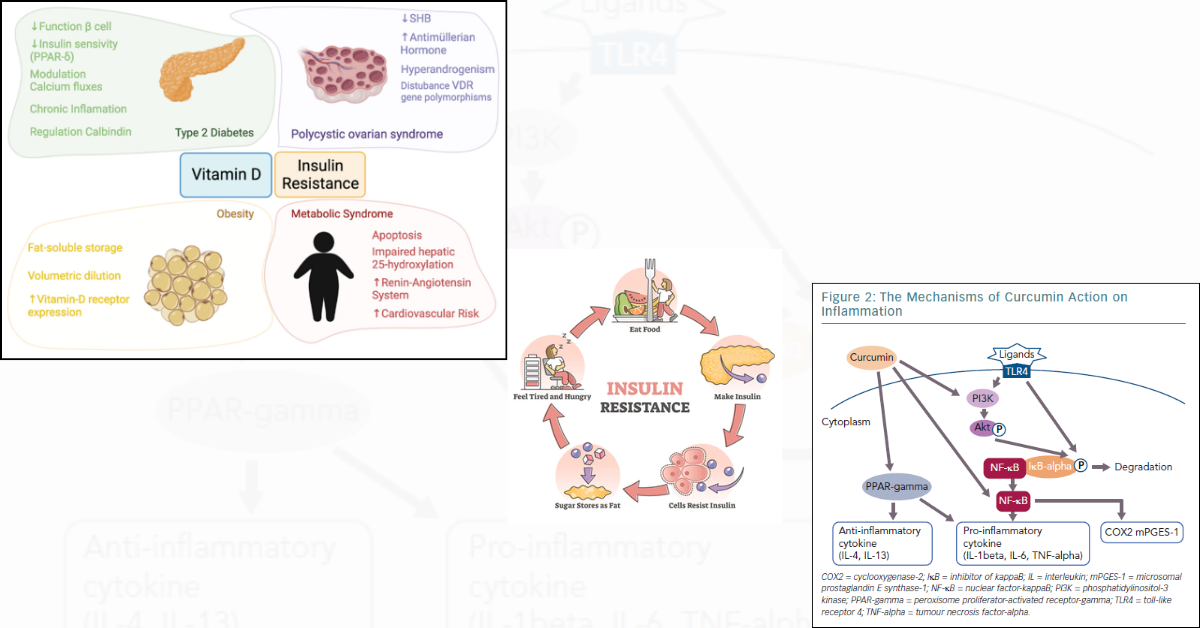
Introduction: Why Diabetes Outcomes Remain Poor Despite Medical Advances
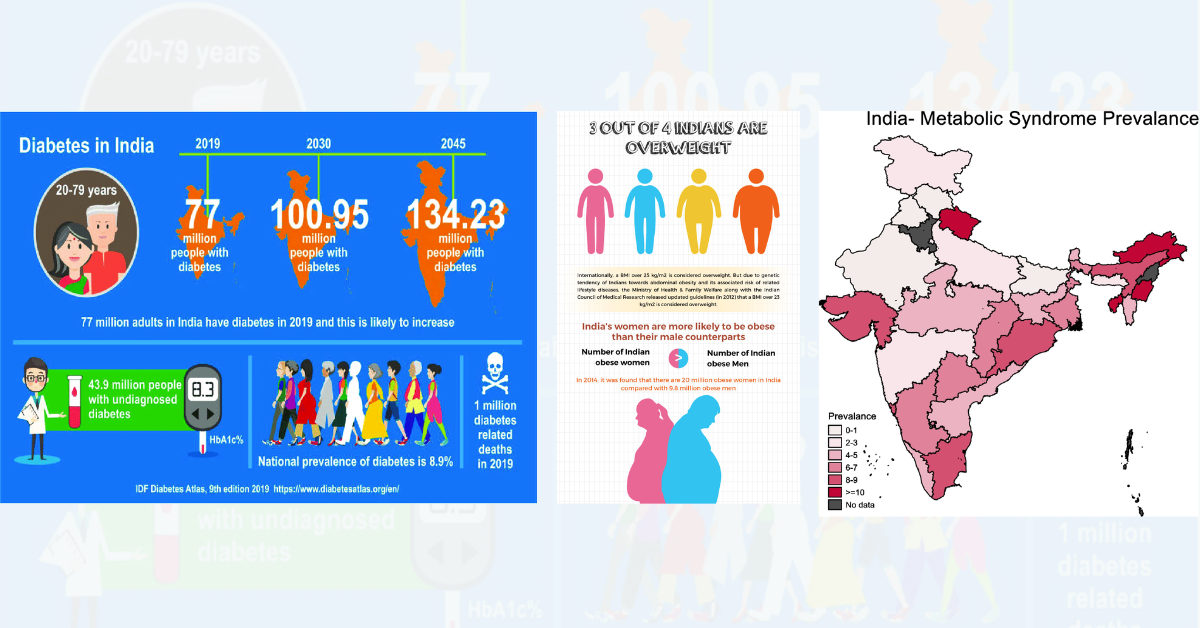
India is often referred to as the diabetes capital of the world, with a rapidly rising burden of type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, central obesity, and associated cardiovascular complications. Over the past two decades, diabetes care has seen an explosion of new drug classes, advanced diagnostics, continuous glucose monitoring, and sophisticated treatment algorithms. Yet, despite these advances, overall morbidity and mortality from diabetes and its complications have not declined proportionately.
Clinicians are increasingly asking a critical question:
Are we missing something fundamental in diabetes management?
Emerging evidence suggests that beyond pharmacotherapy, poor nutritional status, micronutrient deficiencies, oxidative stress, sarcopenia, and gut dysfunction play a decisive role in disease progression, insulin resistance, and complications. Addressing these gaps requires not just adding supplements, but using clinically effective, bioavailable formulations—where liposomal nutraceuticals are gaining relevance.

Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome in India: The Current Landscape
India faces a unique diabetes phenotype characterized by:
- Earlier onset of type 2 diabetes
- Higher prevalence of central (visceral) obesity
- Lower muscle mass relative to fat mass
- Greater insulin resistance at lower BMI
Metabolic syndrome—defined by central obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and impaired glucose regulation—is now common even among young adults. Despite widespread prescribing of antidiabetic medications, long‑term outcomes are limited by:
- Progressive insulin resistance
- Inflammatory burden
- Micronutrient depletion
- Lean muscle loss (sarcopenic or “lean” diabetes)
As Dr. Ramesh (Metabolic Disease Expert, Ramesh Hospital, Vizag) notes:
“We are excellent at lowering glucose numbers, but far less effective at restoring metabolic health. Nutrition, inflammation, and muscle quality are often ignored.”
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome in India: The Growing Challenge
Despite advanced drugs and diagnostics, metabolic outcomes remain suboptimal.
The Hidden Nutritional Deficit in Diabetes
Multiple studies show that people with diabetes and metabolic syndrome frequently have deficiencies in:
- Vitamin D3
- Magnesium
- Iron (functional deficiency)
- Vitamin C
- Antioxidants and mitochondrial cofactors
These deficiencies worsen:
- Insulin resistance
- Beta‑cell stress
- Oxidative damage
- Endothelial dysfunction
Central obesity further aggravates this problem, as adipose tissue acts as an inflammatory organ, sequestering nutrients and impairing their utilization.
According to Dr. HS Ramana (Functional Medicine Specialist, Mysore):
“Correcting micronutrient and antioxidant deficiencies is not optional—it is foundational to improving insulin sensitivity and reducing long‑term complications.”
Why Conventional Supplements Often Fail in Diabetes
Many patients with diabetes take multivitamins, yet clinical benefits remain inconsistent. The reasons include:
- Poor gastrointestinal absorption
- Drug‑nutrient interactions
- Chronic low‑grade inflammation
- Gut dysbiosis and altered permeability
This is where delivery science matters. Liposomal formulations protect nutrients from degradation, enhance absorption, and improve intracellular availability—making them more suitable for metabolically compromised individuals.
Why Glucose Control Alone Is Not Enough
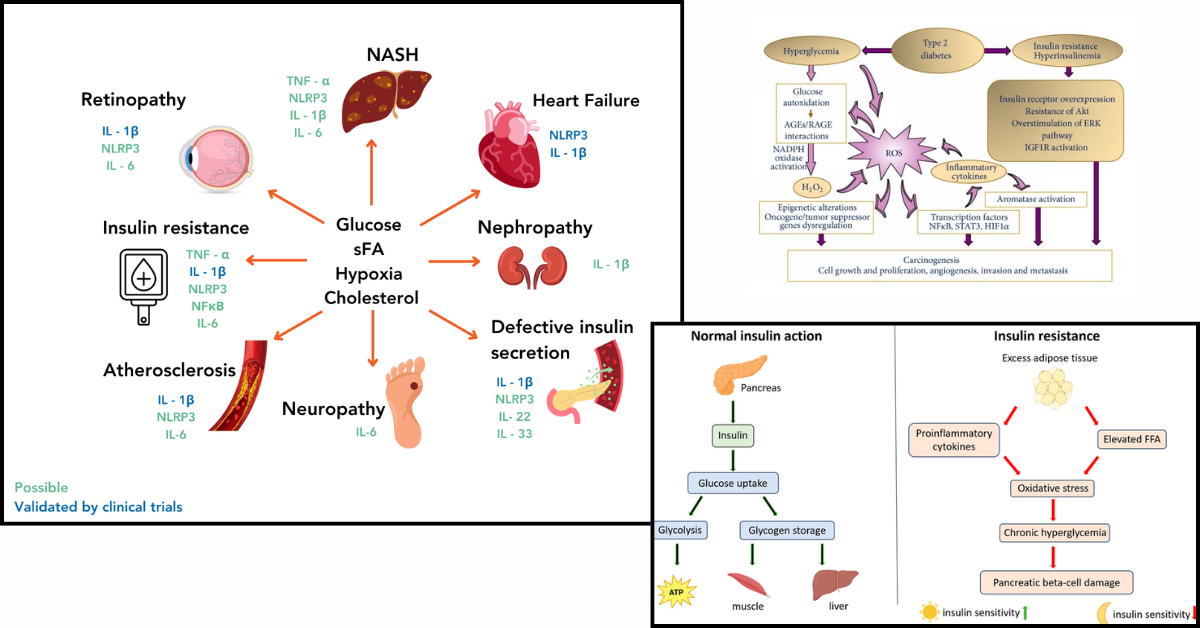
Liposomal Nutraceuticals: A Targeted Metabolic Support Strategy
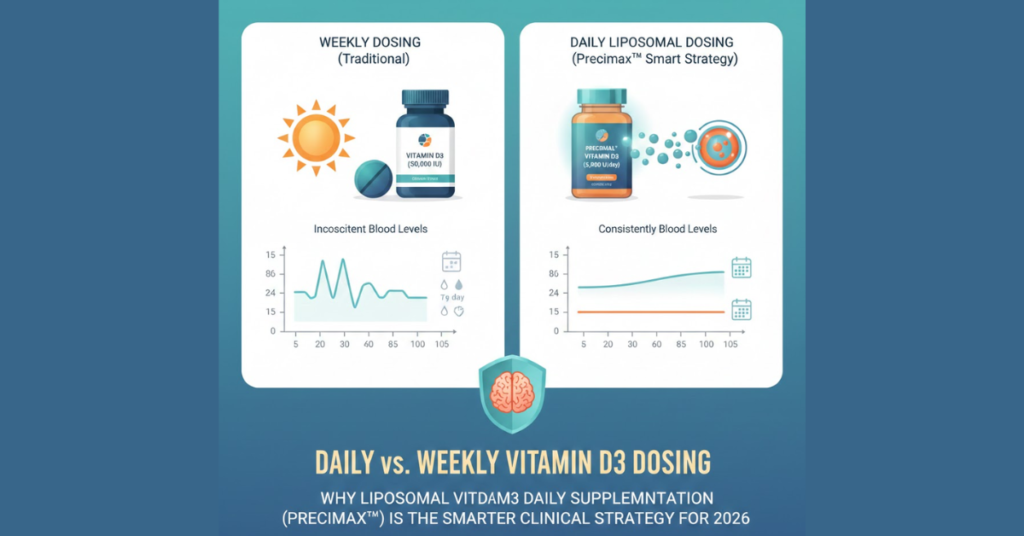
Liposomal Vitamin D3
Vitamin D deficiency is strongly linked to insulin resistance, beta‑cell dysfunction, and immune dysregulation. Liposomal vitamin D3 offers:
- More predictable serum correction
- Better absorption in obese and inflamed states
- Support for insulin secretion and immune balance
Liposomal Magnesium
Magnesium is essential for:
- Insulin receptor signaling
- Glucose transport
- Mitochondrial energy production
Diuretics, metformin, and poor dietary intake often worsen deficiency. Liposomal magnesium improves cellular uptake while reducing gastrointestinal intolerance.
Liposomal Vitamin C
Oxidative stress is a key driver of diabetic complications. Liposomal vitamin C:
- Enhances antioxidant capacity
- Supports endothelial function
- Reduces glycation‑related damage
Liposomal Iron
Functional iron deficiency is common in diabetes due to inflammation‑mediated iron blockade. Liposomal iron improves utilization with fewer gastrointestinal side effects, supporting energy levels and physical capacity.
Liposomal vs Regular Nutraceutical Absorption
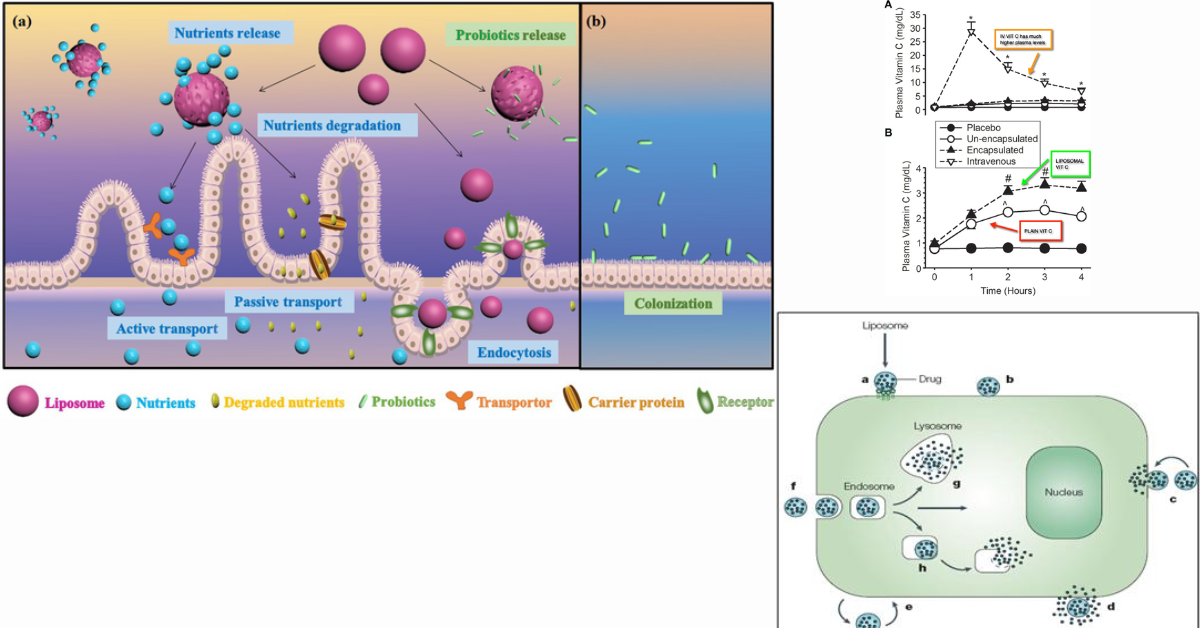
Formulation determines metabolic effectiveness.
Central Obesity, Visceral Fat & the Role of Meal Replacements
Central obesity is not just excess weight—it reflects visceral fat–driven inflammation and insulin resistance. Clinically validated meal replacements such as Precimax Maxlite provide:
- Controlled caloric intake
- High‑quality protein
- Micronutrient completeness
Used strategically, they help reduce visceral fat and support the conversion of white adipose tissue to metabolically active brown adipose tissue, improving insulin sensitivity.
Preserving Muscle Mass: Lean Diabetes & EAA Support
Many Indian patients with diabetes develop sarcopenic or lean diabetes, characterized by low muscle mass and poor strength. High‑quality protein and essential amino acids are critical.
Precimax EAA MAX powder, rich in essential amino acids, helps:
- Preserve lean muscle mass
- Improve insulin‑mediated glucose uptake
- Counter diabetes‑associated catabolic states
Guarding Against Progressive Diabetes: Curcumin & Berberine
Liposomal Berberine
Berberine has shown benefits comparable to metformin in improving insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. Liposomal delivery improves bioavailability and tolerability.
Liposomal Curcumin (Cucimax)
Curcumin modulates:
- Inflammatory cytokines
- Insulin signaling pathways
- Oxidative stress
Precimax Cucimax, a liposomal curcumin formulation, is increasingly used in metabolic syndrome to:
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Reduce inflammatory burden
- Potentially lower long‑term statin dependency in younger patients
Liposomal Curcumin in Diabetic Retinopathy
Chronic hyperglycemia leads to microvascular damage and oxidative stress in the retina. Liposomal curcumin’s anti‑inflammatory and antioxidant effects are particularly relevant in non‑proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Dr. Hasinin Shikhari (Pune) shares:
“I have been using liposomal curcumin (Cucimax) for over five years in patients with early diabetic retinopathy. We observe better inflammatory control and slower disease progression when combined with standard care.”
Cardiometabolic Protection: Liposomal CoQ10
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of mortality in diabetes. Precimax Liposomal CoQ10 (PreciQ10) supports:
- Mitochondrial function
- Endothelial health
- Cardiac energy metabolism
This is particularly relevant for patients on statins, where CoQ10 depletion is common.
Nutraceuticals & Modern Diabetes Drugs: Synergy, Not Substitution
GLP‑1 Analogues (Semaglutide, Tirzepatide)
These agents improve weight loss but may cause:
- Gastrointestinal side effects
- Lean mass loss
- Gut discomfort
Synergistic supports include:
- Prizibiome (high‑quality probiotic) to support gut health
- EAA MAX to preserve muscle mass
- Catechix for metabolic and appetite modulation
Nutraceuticals That Support Insulin Sensitivity
DPP‑4 Inhibitors & Gliptins
Meal replacements like Maxlite help stabilize glycemic variability and support weight management.
Are Liposomal Nutraceuticals Just Adding Cost?
This is a valid concern. However, evidence suggests that high‑quality liposomal nutraceuticals:
- Improve treatment adherence
- Reduce side effects
- Enhance quality of life
- Potentially lower long‑term complication burden
As Dr. Janaki (Diabetologist, Chennai) notes:
“When used judiciously, nutraceuticals are not an added expense—they are an investment in better outcomes.”
Practical Clinical Algorithm
- GLP‑1 analogues → Add Prizibiome + EAA MAX
- Metformin / Pioglitazone → Add Liposomal curcumin (Cucimax)
- Statins → Add Liposomal CoQ10 (PreciQ10)
- Central obesity → Add Meal replacement (Maxlite)
- Micronutrient deficiency → Add Liposomal Vitamin D3, Magnesium, Vitamin C
Central Obesity → Muscle Loss → Lean Diabetes and
ynergy with Modern Diabetes Drugs
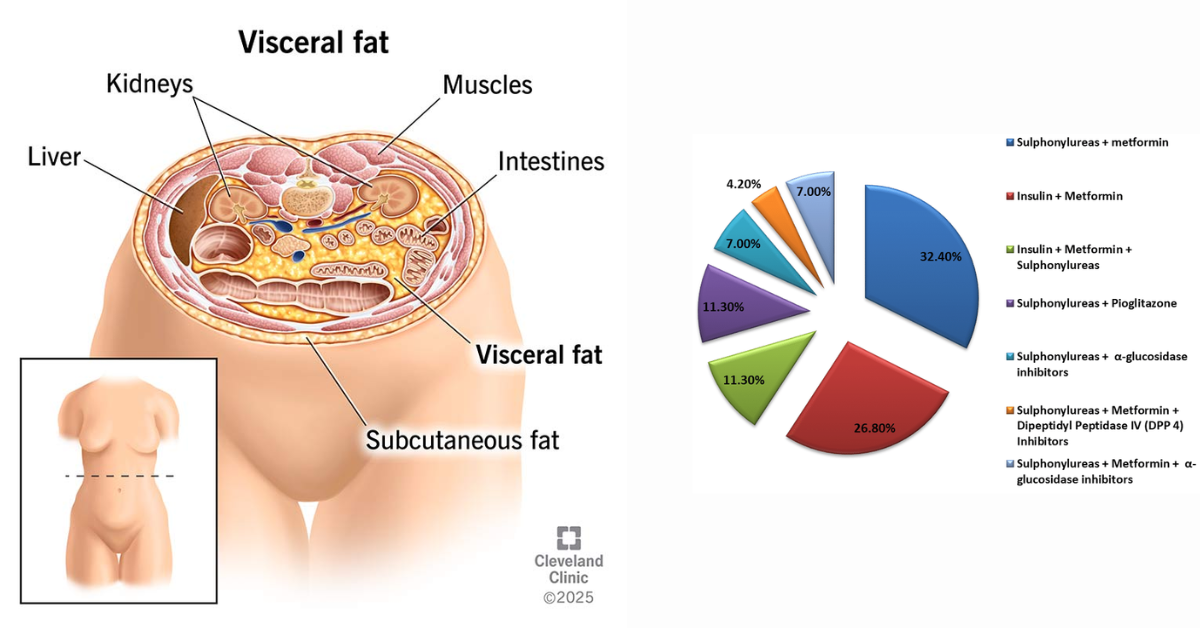
Preserving muscle mass is critical for long‑term diabetes control.
Conclusion: A More Complete Model of Diabetes Care
Diabetes and metabolic syndrome cannot be managed by glucose control alone. Restoring nutritional balance, reducing inflammation, supporting muscle mass, and improving mitochondrial health are essential to meaningful long‑term outcomes.
Liposomal nutraceuticals, when integrated thoughtfully into standard care, offer unique advantages in absorption, tolerability, and clinical impact—helping bridge the gap between biochemical control and real‑world health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Chronic inflammation, drug interactions, poor absorption, and increased metabolic demand contribute to deficiencies.
Yes, liposomal delivery improves intestinal and cellular uptake compared to conventional forms.
Clinical studies associate adequate vitamin D levels with better insulin secretion and sensitivity.
Magnesium supports insulin signaling and glucose metabolism and is often deficient in diabetes.
Yes, through anti‑inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms.
Under medical supervision, it is commonly used as an adjunct.
No. They complement, not replace, prescribed therapy.
Clinically validated meal replacements can be used safely under guidance.
Yes, especially with rapid weight loss, making protein and EAA support important.
They help maintain gut comfort and microbiome balance.
Yes, particularly in statin‑treated patients.
When quality‑controlled and guided, they are generally safe.
They may help reduce GI and fatigue‑related side effects.
Many patients report improved energy and well‑being.
Yes, visceral fat is more metabolically harmful.
They support pathways involved in complication prevention.
Yes, inflammation and oxidative stress are key drivers.
Patients with kidney disease or complex conditions should consult a doctor.
Micronutrient correction may show benefits within weeks; metabolic effects take longer.
Growing evidence and clinical adoption suggest increasing integration into diabetes management.