Creatine Supplement Demystified: Science, Benefits, Limitations, and Why Absorption Matters, Featuring expert insights from Dr. Vinod Raj (Orthopedic Sports Medicine), Dr. Bhavesh (Sports Physiotherapist), Mrs. Lily John (Sports Nutrition Specialist), and Dr. Yoingder (Metabolic Medicine Expert)

Introduction
Creatine Supplement is one of the most researched and scientifically validated supplements in sports nutrition. With over 700 peer-reviewed studies supporting its benefits, creatine monohydrate is widely recognized as a safe, effective, and essential ergogenic aid for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, older adults, and even individuals managing certain metabolic challenges. Yet, confusion, myths, and hesitations remain—largely because many people misunderstand how creatine works, who it is meant for, and why some forms absorb better than others.
With innovative formats such as Precimax Effervescent Creatine Supplement Granules, the landscape of creatine supplementation is changing rapidly. This blog aims to demystify creatine, describe its scientific value, address its limitations, and explain why absorption speed and solubility matter more today than ever before.
Understanding What Creatine Supplement Really Is
Creatine Supplement is a naturally occurring compound found in muscle and brain cells. Approximately 95 percent of the body’s creatine is stored in skeletal muscle, where it helps regenerate ATP—the energy currency needed for high-intensity performance.
The body makes only about 1–2 grams of creatine per day from amino acids such as arginine, glycine, and methionine. For athletes, active individuals, or those seeking cognitive or strength benefits, this natural level is insufficient. Dietary sources like meat and fish provide creatine, but in small quantities, and vegetarian or vegan individuals often have significantly lower baseline creatine levels.
How Creatine Supplement Works: The ATP Regeneration Cycle
During high-intensity exercise such as sprinting, weight training, or rapid bursts of movement, the body relies on ATP. Once ATP is depleted, performance drops sharply. Creatine helps recycle ATP at a much faster rate, allowing longer, stronger, and more powerful effort.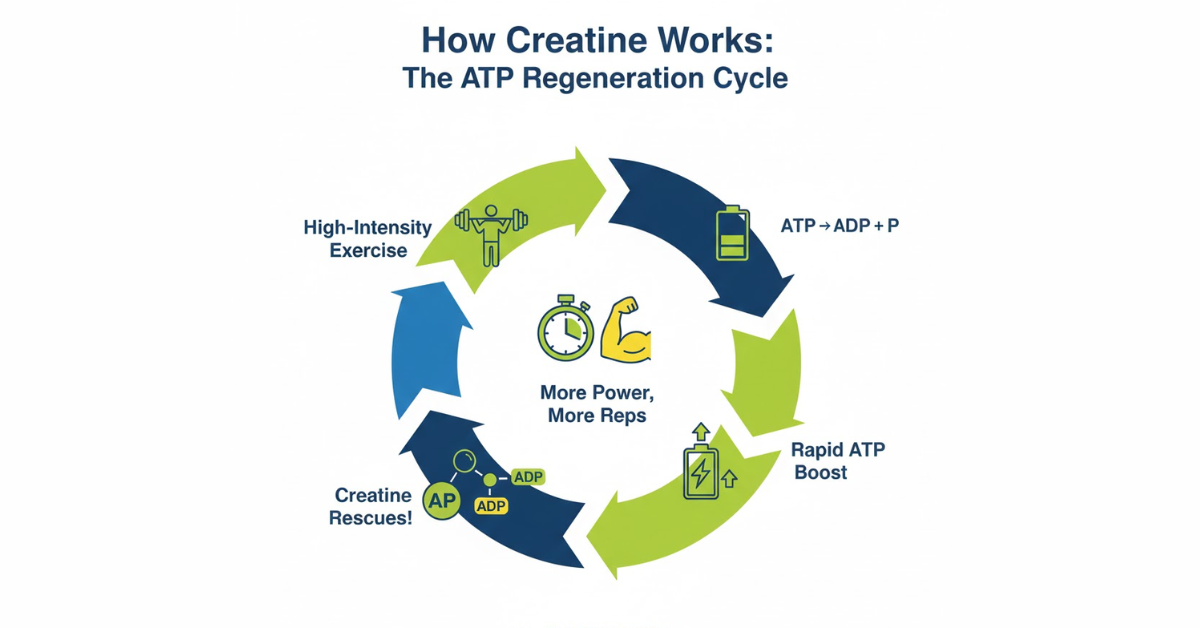
Dr. Vinod Raj, Orthopedic Sports Medicine Specialist, explains:
“Creatine’s impact on ATP regeneration is unmatched. It allows athletes to perform at higher intensity for longer. This is why creatine remains the gold standard in strength, power, and speed disciplines.”
Creatine Supplement’s Benefits: What Science Says
Hundreds of scientific studies show that creatine enhances:
- Strength and power
- Muscle mass and hypertrophy
- Sprint ability
- High-intensity performance
- Recovery after exhaustive exercise
- Brain energy metabolism
- Memory, cognition, and mental fatigue
- Rehabilitation after injury
- Bone density in older adults
Creatine Supplement’s neurological benefits are particularly noteworthy. Research shows improved mitochondrial function, better resilience against mental fatigue, and enhanced cognitive performance during sleep deprivation or stress.

Why Creatine Supplement is Not Just for Bodybuilders
A major misconception is that creatine Supplement is only for heavy lifters. In reality, the individuals who benefit most include:
- Athletes in any high-intensity sport
- Runners and sprinters
- Cyclists
- Football, cricket, and badminton players
- Marathoners (for finishing strength and muscle preservation)
- Post-injury rehabilitation patients
- Older adults with sarcopenia
- Vegetarians and vegans (low baseline creatine)
- People with high cognitive demands (students, night workers, professionals)
Mrs. Lily John, Sports Nutrition Specialist, notes:
“When I test athletes for strength output or muscle endurance, those who supplement with creatine consistently outperform those who don’t. Even non-athletes—especially older adults and vegetarians—see significant improvements in energy and muscle health.”
Limitations of Conventional Creatine Supplement Powders
Despite its benefits, traditional creatine monohydrate powders come with limitations:
- Poor solubility: Many users complain that creatine powder settles at the bottom of the glass.
- Slow absorption: Because it does not dissolve completely, the absorption rate is delayed.
- Digestive discomfort: Some experience bloating, heaviness, or mild stomach irritation.
- Timing sensitivity: Creatine absorbs better on an empty stomach but may cause discomfort when taken this way.
- Gritty taste or texture: The sandy mouthfeel reduces compliance.
Dr. Bhavesh, Sports Physiotherapist who works with marathoners, adds:
“Many endurance athletes avoid creatine because they find conventional powders uncomfortable or heavy. But this is actually a limitation of the delivery form, not creatine itself.”
Why Absorption Speed Matters
Fast absorption determines how quickly creatine enters the bloodstream and muscle tissue. Slow-dissolving powders lead to variable uptake, which means users may not achieve full saturation.
Precimax Effervescent Creatine Supplement Granules solve this issue.
The effervescent technology pre-dissolves creatine almost instantly, converting it into a readily absorbable ionic form. This gives:
- Better absorption
- Faster onset of action
- No stomach irritation
- No gritty texture
- More predictable performance results
Dr. Yoingder, Metabolic Medicine Specialist, explains:
“Absorption determines efficacy. Effervescent creatine provides superior bioavailability with less digestive stress. This makes it suitable even for metabolic patients who are typically sensitive to supplement load.”
Scientific Applications of Creatine Supplement
Creatine Supplement’s applications extend beyond sport.
- Sports performance
Improved sprint output, explosive movements, peak strength. - Injury rehabilitation
Faster recovery of muscle mass
Reduced fatigue during physiotherapy
Improved limb strength post-immobilization - Cognitive performance
Improved memory
Better mental clarity
Reduced brain fatigue - Aging and sarcopenia
Creatine improves protein synthesis and reduces age-related muscle loss.
Creatine Supplement and Brain Function: A New Frontier

Brain cells use ATP just like muscle cells. Creatine Supplement supports mitochondrial energy, making it useful for:
- Students
- Shift workers
- Individuals under mental stress
- People recovering from neurological conditions
Compared to protein supplements, creatine has a direct effect on energy metabolism—not just muscle repair.
Who Should Take Creatine Supplement?
Creatine Supplement is ideal for:
- Athletes needing explosive performance
- Gym-goers aiming for strength and size
- People doing HIIT or CrossFit
- Marathoners (for late-race strength)
- Adults over 40 with muscle loss
- Vegetarians or vegans
- Individuals in cognitive-demanding jobs
- Rehab patients recovering muscle strength
Who Should Avoid Creatine Supplement?
Creatine Supplement is safe for most individuals, but contraindications include:
- Severe kidney disease
- Active renal dysfunction
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Recurrent dehydration
- People advised to avoid high water intake
Those with medical conditions should consult their physician.

Ideal Duration of Use
Creatine Supplement works best with consistent use.
Typical duration:
- Loading phase: optional
- Saturation phase: 4–8 weeks
- Maintenance: 3–6 months
- Break: 2–4 weeks (optional)
Effervescent creatine reaches saturation faster, so loading is usually unnecessary.
Dosing Guideline
Effervescent creatine granules:
3–5 g per day, ideally post-workout
On rest days: morning on an empty stomach or with a light carb source
Precimax Effervescent Creatine Supplement Granules: Why This Innovation Matters
Traditional powders are effective but limited by solubility and stomach comfort.
Precimax solves these problems with:
- Fast dissolving technology
- Superior absorption
- No grit, no foam, no heaviness
- Better tolerance for endurance athletes and women
- Perfect for rehab patients who need gentle supplementation
- Ideal for those who dislike conventional powder textures
FAQs
- Is creatine safe for daily use?
Yes. Creatine monohydrate is one of the safest long-term supplements ever studied. - Will creatine make me gain weight?
It may increase muscle hydration, which is healthy. Not fat gain. - Do women benefit from creatine?
Absolutely. Women often have lower baseline creatine levels and respond very well. - Can creatine help endurance athletes?
Yes. Creatine improves finishing strength, reduces muscle breakdown, and improves recovery. - Is creatine suitable for older adults?
Yes. It supports muscle mass, balance, and prevents age-related muscle loss. - Does creatine harm the kidneys?
Only individuals with existing severe kidney disease should avoid it. - Can creatine be combined with protein supplements?
Yes. Creatine and protein work through different pathways and complement each other. - Should vegetarians take creatine?
Vegetarians often have lower creatine stores and benefit greatly from supplementation. - What makes effervescent creatine better?
Superior solubility, faster absorption, improved stomach comfort and better performance outcomes.
Conclusion
Creatine is powerful, safe, and clinically validated. It benefits athletes, everyday exercisers, older adults, cognitive performers, and rehabilitation patients. However, traditional creatine powders come with absorption and comfort limitations. Precimax Effervescent Creatine Granules deliver a next-generation solution—fast-absorbing, gentle on the stomach, and ideal for a wide range of users.