Introduction: Why Oxidative Stress Has Become Central to Modern Disease Management
Oxidative stress is now widely recognized as one of the most important biochemical drivers behind chronic lifestyle diseases. From diabetes and cardiovascular disorders to neurodegeneration, autoimmune dysregulation, accelerated aging, and immune decline, a common mechanistic thread continues to emerge:

An imbalance between oxidative damage and antioxidant defense.
India is witnessing a sharp rise in metabolic syndrome, early‑onset type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease, osteoarthritis, and cardiovascular mortality. Despite major advances in medical diagnostics and drug therapies, morbidity remains high.
The clinical reality is clear:
- We have more tests
- More specialists
- More medicines
- Yet complications continue to rise
This has shifted attention toward deeper physiological mechanisms such as:
- chronic inflammation
- mitochondrial dysfunction
- oxidative stress overload
- micronutrient depletion
Increasingly, clinicians are recognizing that antioxidant support is not “wellness marketing” but a scientifically relevant axis of disease prevention.
However, a persistent limitation remains:
Most antioxidant supplements fail to provide consistent clinical outcomes due to poor absorption and weak bioavailability.
This is precisely where liposomal antioxidants represent a major emerging trend in functional and preventive medicine.
What Exactly Is Oxidative Stress?
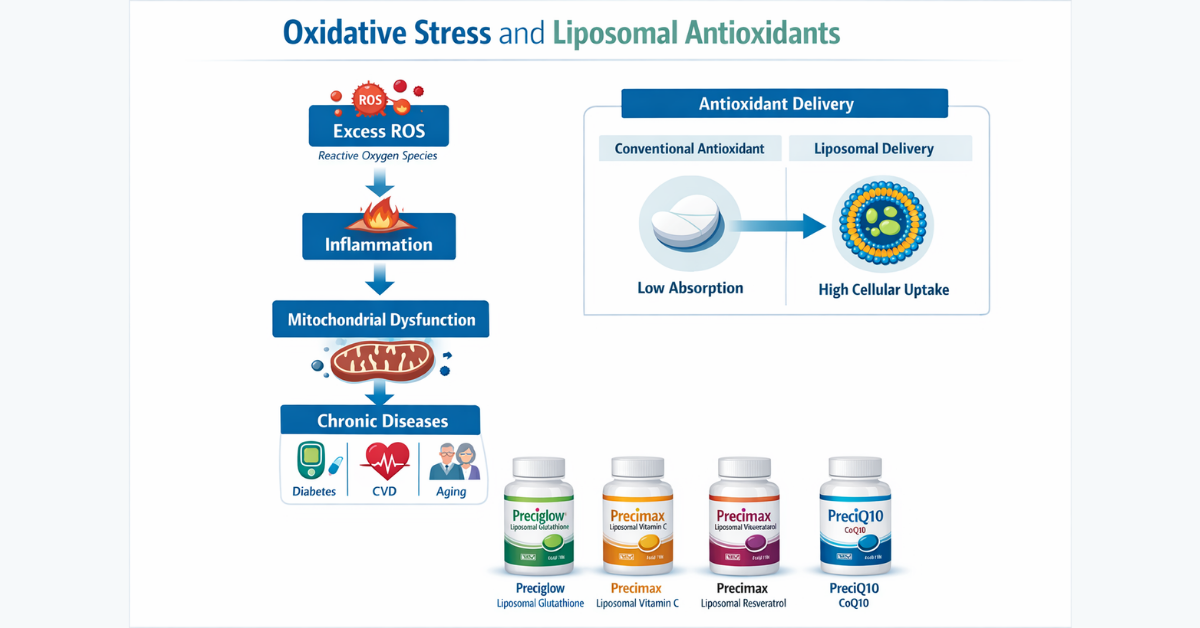
Oxidative stress occurs when reactive oxygen species (ROS) overwhelm the body’s antioxidant defense systems.
ROS are continuously generated through:
- hyperglycemia
- insulin resistance
- obesity‑driven inflammation
- pollution exposure
- poor sleep
- chronic stress
- aging mitochondria
- infections and post‑viral inflammatory states
When oxidative stress persists, it damages:
- DNA
- cell membranes
- proteins
- mitochondria
- vascular endothelium
This accelerates progression of:
- diabetic complications
- cardiovascular plaque instability
- cartilage degeneration
- liver inflammation
- neurodegenerative decline
Why Oxidative Stress Matters Even More in India
India’s oxidative stress burden is amplified by unique systemic realities:
- early diabetes at younger age
- central obesity at low BMI
- nutrient‑poor diets
- high pollution exposure
- persistent vitamin D, magnesium, antioxidant deficiencies
- high triglycerides + low HDL phenotype
As Dr Vinod Jain (Metabolic Specialist, Bangalore) explains:
“In Indian metabolic patients, oxidative stress and endothelial inflammation begin years before clinical heart disease. Numbers like glucose and cholesterol matter, but oxidative injury is the silent accelerator behind complications.”
The Antioxidant Paradox: Strong Evidence, Poor Results
Antioxidants such as glutathione, curcumin, resveratrol, CoQ10 and vitamin C have extensive mechanistic support.
Yet many patients report:
- inconsistent symptom relief
- no biomarker improvement
- poor tolerability
The reason is not lack of scientific activity.
It is delivery failure.
Most traditional antioxidant nutraceuticals face pharmacological limitations:
- poor solubility
- acid degradation
- low intestinal permeability
- rapid hepatic metabolism
- inability to reach therapeutic plasma levels
This leads to:
- need for very high doses
- gastrointestinal intolerance
- unpredictable clinical performance
As Dr Sundar (Head – R&D, Precimax Life Sciences) notes:
“Antioxidants are among the most validated molecules in preventive medicine. But unless delivery systems overcome absorption barriers, real‑world consistency remains difficult. Clinical reliability depends more on formulation than ingredient label.”
Emerging Trend: Liposomal Antioxidants as a Clinical Upgrade
Liposomal delivery encapsulates actives inside phospholipid bilayers — structurally similar to human cell membranes.
This offers:
- protection from stomach acid
- enhanced absorption through gut lining
- improved cellular uptake
- better plasma persistence
- lower dose requirements
- reduced GI irritation
This is why liposomal antioxidants are increasingly being integrated into:
- metabolic protocols
- cardiometabolic risk reduction
- longevity medicine
- neuroprotection strategies
- post‑viral recovery
Precimax Liposomal Antioxidant Range: Clinically Relevant Actives
1. Liposomal Glutathione (Preciglow)
Glutathione is often called the body’s master antioxidant, central to:
- detoxification
- immune defense
- hepatic protection
- cellular repair
- oxidative aging control
Conventional oral glutathione is degraded before systemic benefit.
Liposomal glutathione (Preciglow) improves plasma availability and is used clinically in:
- chronic fatigue syndromes
- oxidative stress overload
- metabolic inflammation
- longevity protocols
Dr Jeethan (Anti‑Aging Specialist, Pune) adds:
“In longevity practice, we increasingly see oxidative stress as the true driver of aging. Liposomal glutathione has become foundational because it restores antioxidant capacity at the cellular level, not just in theory.”
2. Liposomal Vitamin C (Precimax Liposomal Vitamin C)
Vitamin C is crucial for:
- immune antioxidant defense
- collagen stability
- endothelial protection
- glycation control
Traditional oral vitamin C has saturable absorption at higher doses.
Liposomal vitamin C improves systemic exposure while reducing GI irritation, making it clinically useful in:
- post‑viral recovery
- metabolic oxidative stress
- vascular fragility
3. Liposomal Curcumin (Cucimax)
Curcumin is one of the world’s most studied anti‑inflammatory antioxidants.
It modulates:
- NF‑κB
- cytokine cascades
- oxidative stress mediators
Yet standard curcumin is famously poorly absorbed.
Micellar / Liposomal Curcumin (Cucimax) achieves higher plasma exposure, supporting:
- metabolic syndrome protocols
- osteoarthritis inflammation control
- fatty liver modulation
Dr Vinod Jain comments:
“In fatty liver and insulin resistance, oxidative stress drives hepatocyte injury. Bioavailable curcumin can be an important adjunct, especially when patients cannot tolerate long‑term drug escalation.”
Oxidative Stress in Osteoarthritis: Cartilage Breakdown Beyond “Wear and Tear”
Osteoarthritis is not simply mechanical degeneration.
Oxidative stress accelerates:
- cartilage matrix breakdown
- inflammatory cytokine release
- pain sensitization
Dr Sundar notes:
“In osteoarthritis, oxidative injury contributes directly to cartilage destruction. Liposomal curcumin provides a way to modulate this inflammation consistently without depending on high oral doses.”
4. Liposomal Resveratrol (Precimax Liposomal Resveratrol)
Resveratrol is valued for:
- endothelial function
- longevity pathways (SIRT activation)
- mitochondrial protection
- neuroprotection
However, traditional resveratrol is rapidly metabolized.
Precimax Liposomal Resveratrol enhances plasma persistence.
Dr Jeethan adds:
“Resveratrol is one of the most exciting longevity molecules, but delivery is everything. Liposomal formulations finally allow it to reach clinically meaningful levels.”
5. Liposomal CoQ10 (PreciQ10)
CoQ10 is essential for:
- mitochondrial ATP production
- cardiac energy metabolism
- endothelial stability
Deficiency is common in:
- statin users
- diabetics
- aging individuals
PreciQ10 (liposomal CoQ10) supports mitochondrial function — particularly relevant in neurodegeneration.
Dr Vinod Jain emphasizes:
“Neurodegenerative diseases and diabetic neuropathy share mitochondrial dysfunction as a core mechanism. CoQ10 delivery is one of the most clinically meaningful antioxidant strategies.”
6. Liposomal Melatonin (Precimax Liposomal Melatonin)
Melatonin is not only a sleep hormone but also a powerful antioxidant.
It supports:
- neuroinflammation reduction
- mitochondrial repair
- immune regulation
Liposomal delivery improves predictability and reduces next‑day sedation.
Expanded Clinical Applications: Where Liposomal Antioxidants Matter Most
Diabetic Retinopathy Prevention
Diabetic retinopathy progression is driven by:
- oxidative vascular injury
- inflammatory cytokines
- microvascular dysfunction
Dr Sundar explains:
“Early diabetic retinopathy is fundamentally an oxidative microvascular disorder. Bioavailable antioxidants such as liposomal curcumin and glutathione may support retinal protection when integrated early alongside standard care.”
Dyslipidemia: Low HDL + High Triglycerides
India’s typical dyslipidemia phenotype is oxidative and inflammatory.
Liposomal resveratrol and CoQ10 support:
- endothelial resilience
- mitochondrial lipid metabolism
- oxidative lipid control
Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD progression is strongly oxidative:
- ROS accumulation
- hepatocyte injury
- fibrosis signaling
Curcumin + glutathione combinations are increasingly integrated in preventive liver protocols.
Neurodegeneration and Cognitive Decline
Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are central to:
- Parkinson’s
- Alzheimer’s
- diabetic neuropathy
Liposomal CoQ10 is particularly valuable as mitochondrial support.
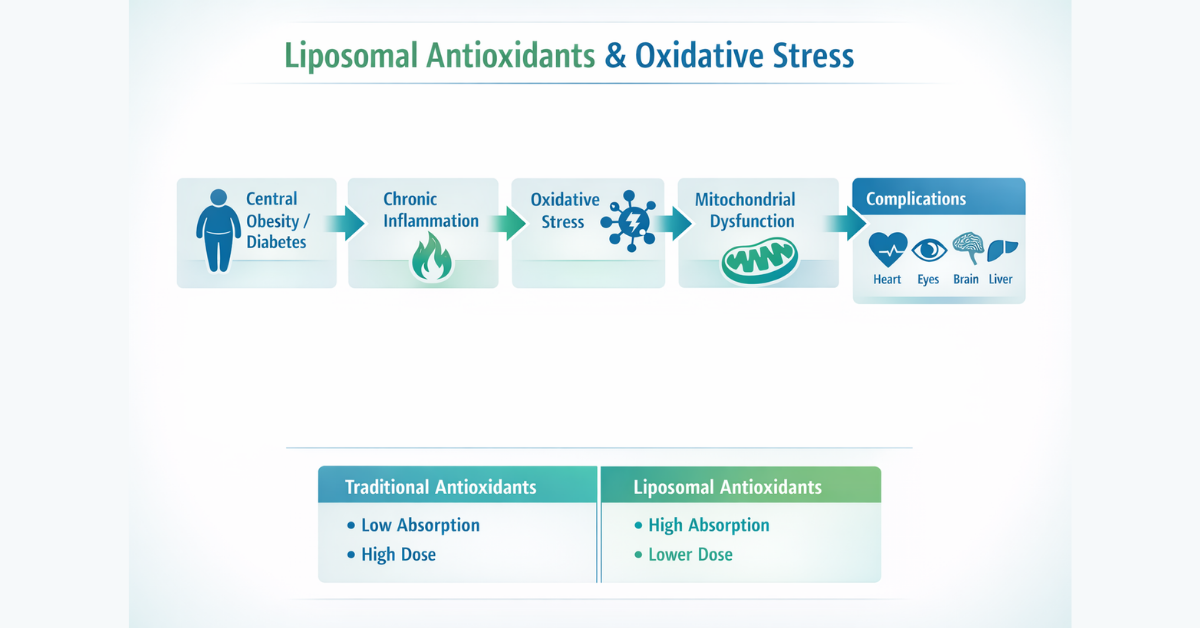
Traditional vs Liposomal Antioxidants
| Parameter | Traditional Supplements | Liposomal Antioxidants |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption | Variable, low | High, predictable |
| Dose needed | Higher | Lower |
| GI side effects | Common | Reduced |
| Plasma consistency | Unreliable | Stable |
| Cellular uptake | Limited | Enhanced |
Passive vs Active Nutraceutical Strategy
| Approach | Passive Nutraceuticals | Active Liposomal Nutraceuticals |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | General wellness | Clinical modulation |
| Evidence translation | Weak | Stronger |
| Target outcomes | Maintenance | Predictable correction |
| Best use | Healthy individuals | Chronic metabolic patients |
Disease Applications
| Condition | Traditional Outcome | Liposomal Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes oxidative stress | Inconsistent benefit | Better cellular delivery |
| Osteoarthritis | Needs high doses | Lower-dose anti-inflammatory support |
| Fatty liver | Limited correction | Enhanced antioxidant modulation |
| Neurodegeneration | Poor uptake | Mitochondrial targeting |
 Final Take‑Home Message
Final Take‑Home Message
Oxidative stress is no longer a theoretical concept — it is a measurable, central driver of India’s chronic disease burden.
Liposomal antioxidants represent an evidence‑driven formulation shift that allows antioxidants to work at clinically meaningful levels.
Dr Sundar concludes:
“The future of nutraceuticals is not about adding more ingredients — it is about delivering the right molecule in the right form for predictable outcomes.”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Oxidative stress is excess free radical damage overwhelming antioxidant defenses.
It drives vascular injury and complications like neuropathy and retinopathy.
Poor absorption and rapid metabolism prevent consistent plasma levels.
They are nutrients encapsulated for enhanced absorption and cellular delivery.
Yes, it bypasses degradation and improves systemic antioxidant levels.
Cellular antioxidant restoration, fatigue, recovery, longevity support.
Yes, especially in liposomal form for systemic oxidative control.
Curcumin modulates inflammatory pathways central to chronic disease.
It provides bioavailable curcumin with reliable absorption.
Endothelial protection, longevity pathways, neuroprotection.
Improved persistence and clinical predictability.
It supports mitochondrial ATP production and cardiac health.
Enhanced mitochondrial delivery in statin users and diabetics.
Yes, especially neuroprotective and mitochondrial supportive.
Yes, when quality-controlled and clinically guided.
Often yes, due to lower doses and better outcomes.
No, they complement standard therapy.
Yes, oxidative stress accelerates cartilage degeneration.
They support oxidative modulation alongside lifestyle therapy.
Clinical adoption strongly suggests yes.




