Introduction: Why Sleep and Stress Disorders Are Rising Rapidly in India
India is currently witnessing an unprecedented rise in sleep disturbances, chronic stress, anxiety‑linked fatigue, and neuroinflammatory brain health disorders. What was once considered a lifestyle inconvenience has now become a major public health burden affecting:
- Productivity
- Mental resilience
- Hormonal balance
- Cardiovascular risk
- Long‑term cognitive aging
From corporate burnout in urban India to sleep deprivation in rural working populations, the crisis is widespread.
Modern science now confirms:
Sleep disruption is not just “tiredness.”
It is a neuroinflammatory state that accelerates aging and chronic disease.
Despite increasing prescriptions for sedatives, antidepressants, and sleep aids, long‑term outcomes remain limited because the underlying drivers—oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, micronutrient depletion, and neuroinflammation—are often ignored.
This is where innovative liposomal nutraceuticals are emerging as evidence‑based tools in preventive neurology and functional medicine.
Sleep, Stress & Neuroinflammation: The Growing Epidemic
Why is this increasing?
India’s modern lifestyle amplifies stress biology through:
- Long screen exposure
- Digital overstimulation
- Night‑shift work
- Poor sunlight exposure
- Metabolic syndrome
- Urban pollution
- Chronic inflammation
Stress triggers excessive cortisol release, which directly disrupts:
- Melatonin cycles
- Sleep depth
- Neurotransmitter balance
- Memory consolidation
Over time, this fuels brain inflammation.
Neuroinflammation: The Missing Link Between Stress and Brain Decline
Neuroinflammation refers to chronic immune activation within the nervous system.
It is increasingly associated with:
- Depression and anxiety
- Cognitive slowing
- Alzheimer’s disease risk
- Parkinsonian changes
- Sleep fragmentation
- “Brain fog” syndromes
- Post‑viral fatigue
Stress, obesity, and diabetes all accelerate neuroinflammatory cascades through oxidative stress.
Consequences: How Poor Sleep Accelerates Aging and Disease
Sleep loss does not remain confined to tiredness. It contributes to:
- Elevated blood pressure
- Insulin resistance
- Weight gain
- Reduced immunity
- Increased cardiac mortality
- Accelerated skin and cellular aging
- Neurodegenerative vulnerability
In younger adults, chronic stress leads to reduced productivity and emotional instability.
In older adults, it contributes to cognitive decline.
Rural vs Urban Divide, Male vs Female Burden
Urban India
- High burnout, insomnia, anxiety
- Technology‑driven circadian disruption
- Obesity and metabolic inflammation
Rural India
- Sleep deprivation due to labor demands
- Poor nutrition and micronutrient deficiency
- Limited mental health access
Women
Higher prevalence of anxiety, hormonal sleep disruption, iron deficiency fatigue
Men
Higher metabolic syndrome linked insomnia, alcohol‑related sleep disturbances
Thus, sleep health is now a national wellness priority.
Why Conventional Approaches Often Fall Short
Most conventional sleep treatments focus on symptom suppression:
- Sedatives
- Anxiolytics
- Antidepressants
Limitations include:
- Dependency risk
- Morning grogginess
- No correction of oxidative brain injury
- No mitochondrial restoration
Functional medicine emphasizes that improving sleep requires repairing neurobiology, not only sedation.
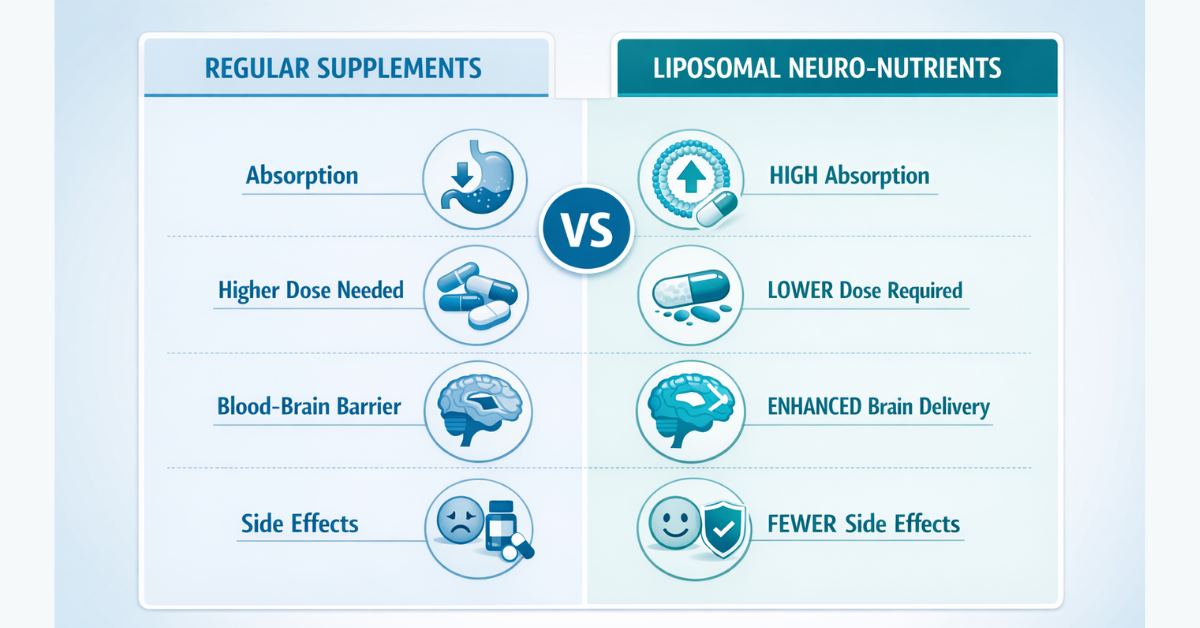
Why Liposomal Nutraceuticals Are an Emerging Trend
Liposomal formulations encapsulate nutrients in phospholipid nanoparticles, offering:
✅ Higher bioavailability
✅ Better penetration into tissues
✅ Potential BBB (blood‑brain barrier) support
✅ Sustained release action
✅ Lower dose effectiveness
✅ Reduced gastrointestinal side effects
This makes them particularly relevant for neuroinflammatory disorders.
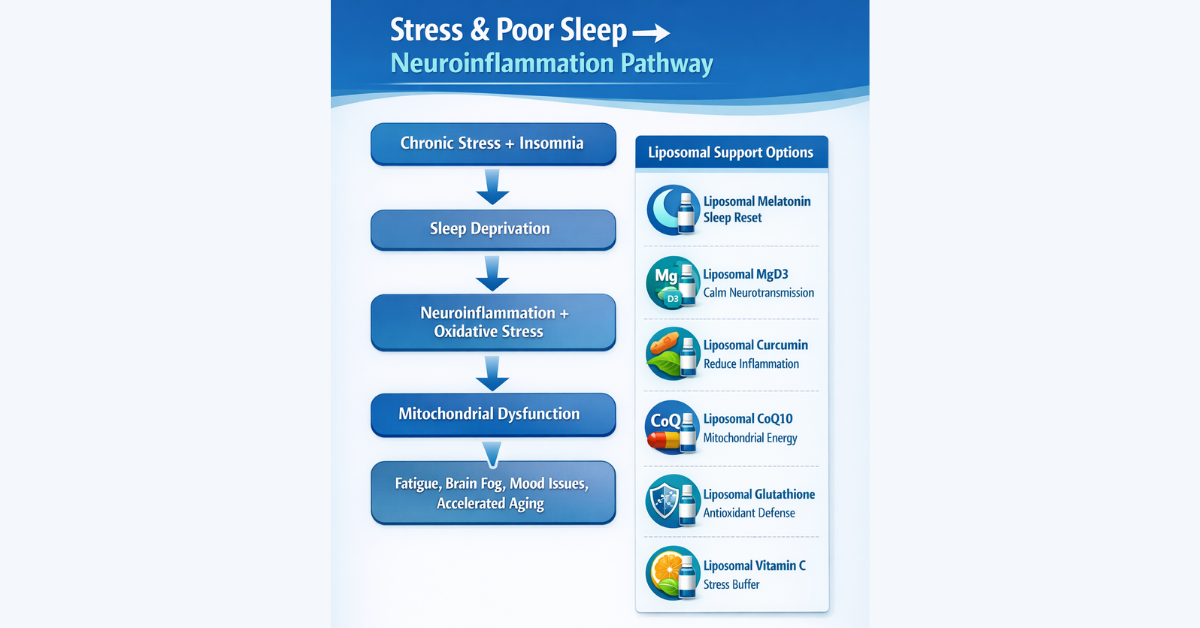
Key Liposomal Nutraceuticals in Sleep, Stress & Brain Inflammation
A. Liposomal Melatonin (Precimax Liposomal Melatonin)
Melatonin is not only a sleep hormone—it is also a powerful brain antioxidant.
Benefits include:
- Improved sleep onset
- Better circadian rhythm restoration
- Neuroprotective antioxidant defense
- Reduced neuroinflammatory burden
Liposomal delivery improves predictability at lower doses.
B. Liposomal CoQ10 (PreciQ10): Mitochondrial Brain Support
CoQ10 is essential for mitochondrial ATP production.
Low CoQ10 levels are linked to:
- Fatigue syndromes
- Cognitive slowing
- Neurodegeneration
- Statin‑associated brain fog
PreciQ10 supports mitochondrial resilience, relevant in aging neurology.
C. Liposomal MgD3: Magnesium + Vitamin D3 + K2‑7
Magnesium is foundational for:
- GABA calming neurotransmission
- Muscle relaxation
- Stress resilience
- Sleep depth improvement
Vitamin D3 deficiency worsens:
- depression risk
- inflammation
- insomnia
Liposomal MgD3 provides predictable cellular absorption.
D. Liposomal Curcumin (Cucimax): Neuroinflammation Modulator
Curcumin is one of the world’s best‑studied anti‑inflammatory compounds, linked to:
- Reduced cytokine activity
- Neuroprotective pathways
- Alzheimer’s support mechanisms
- Mood stabilization
Standard curcumin has poor absorption.
Cucimax (liposomal curcumin) achieves clinically meaningful bioavailability.
E. Liposomal Vitamin C
Vitamin C supports:
- Cortisol regulation
- Oxidative stress control
- Immune‑brain resilience
Liposomal vitamin C avoids GI intolerance at higher antioxidant doses.
F. Preciglow (Liposomal Glutathione)
Glutathione is the body’s master antioxidant, relevant in:
- Post‑viral fatigue
- Chronic stress syndromes
- Cognitive inflammation
- Cellular aging
Preciglow supports systemic oxidative balance.
Who Benefits Most from Liposomal Brain‑Support Nutraceuticals?
- Individuals with chronic insomnia
- High‑stress professionals
- Women with hormonal fatigue and anxiety
- Elderly patients with cognitive decline risk
- Post‑viral brain fog patients
- Metabolic syndrome patients with sleep apnea and inflammation
When to Start, When to Stop, When to Consult a Doctor
Start when:
- Persistent sleep disturbance >3 weeks
- Fatigue with stress overload
- Biomarkers show deficiency (D3, magnesium)
Stop/adjust when:
- Sleep normalizes consistently
- Biomarkers corrected
Doctor supervision required for:
- Pregnancy
- Autoimmune disease
- Severe depression or psychiatric illness
- Patients on sedatives or anticoagulants
Future Treatment Protocols: Functional Neurology + Liposomal Precision Nutrition
The future of brain health will combine:
- Conventional therapies
- Lifestyle correction
- Nutrient bioavailability science
- Neuroinflammation reduction
Liposomal nutraceuticals represent a bridge between preventive neurology and personalized medicine.
Conclusion: The Next Era of Brain Wellness is Bioavailability‑Driven
Sleep and stress disorders are now neuroinflammatory conditions, not merely lifestyle inconvenience. Liposomal nutraceuticals offer a scientifically aligned strategy to improve:
- Sleep architecture
- Brain antioxidant defense
- Mitochondrial resilience
- Long‑term cognitive protection
Precimax’s liposomal portfolio represents this future of evidence‑based preventive neuroscience.
Mechanism of Action: Liposomal Coenzyme Q10 in Neurodegeneration (Published Evidence)
Why CoQ10 Matters in Brain Aging
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a critical mitochondrial cofactor involved in:
- ATP (energy) production
- Electron transport chain stabilization
- Antioxidant defense inside neurons
Neurodegenerative disorders such as:
- Parkinson’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Huntington’s disease
- ALS
- Diabetic neuropathy
share one common mechanism:
Mitochondrial dysfunction + oxidative neuronal injury
Mechanisms by Which CoQ10 Supports Neuroprotection
1. Restores Mitochondrial Energy Output
Neurons have extremely high energy requirements.
CoQ10 supports:
- Complex I–III electron transfer
- ATP synthesis
- Neuronal survival signaling
Key published concept:
Mitochondrial ATP failure precedes neuronal degeneration.
2. Reduces Oxidative Stress in CNS
CoQ10 is one of the body’s strongest lipid‑phase antioxidants.
It prevents:
- Lipid peroxidation in neuronal membranes
- Mitochondrial ROS overload
- Oxidative DNA damage
Oxidative injury is central in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s pathology.
3. Stabilizes Neuroinflammation Pathways
CoQ10 reduces neuroinflammatory mediators such as:
- TNF‑α
- IL‑6
- NF‑κB activation
Thus, it acts as an anti‑inflammatory mitochondrial modulator.
4. Protects Against Apoptosis (Neuron Cell Death)
CoQ10 supports mitochondrial membrane stability and prevents:
- Cytochrome‑c leakage
- Caspase activation
- Neuronal apoptosis progression
Why Liposomal CoQ10 Has Higher Clinical Relevance
Conventional CoQ10 has poor absorption because it is:
- Highly lipophilic
- Large molecular weight
- Low intestinal uptake
Liposomal CoQ10 improves:
✅ Plasma bioavailability
✅ Cellular uptake into mitochondria
✅ Brain tissue delivery potential
✅ Lower dose effectiveness
Thus, liposomal CoQ10 is considered an emerging functional neurology tool.
Clinical Evidence
“Coenzyme Q10 and Neurodegenerative Disorders: Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Therapeutic Potential”
“CoQ10 Supplementation in Parkinson’s Disease: Effects on Mitochondrial Bioenergetics”
“Oxidative Stress and Coenzyme Q10 in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis”
Mechanism of Liposomal Curcumin in MDD and Bipolar Disorder (Literature Evidence)
Depression Is Increasingly a Neuroinflammatory Disorder
Modern psychiatry recognizes that major depression is not only neurotransmitter imbalance, but also involves:
- Neuroinflammation
- Oxidative stress
- Gut–brain axis disruption
- HPA‑axis cortisol dysregulation
Bipolar disorder shows similar inflammatory patterns during mood episodes.
Curcumin’s Mechanisms in Mood Disorders
1. Anti‑Inflammatory Modulation (NF‑κB Pathway)
Curcumin suppresses inflammatory transcription pathways:
- NF‑κB
- COX‑2
- IL‑1β, IL‑6, TNF‑α
High cytokine states are strongly linked with treatment‑resistant depression.
2. Antioxidant Neuroprotection
Curcumin increases endogenous antioxidant enzymes:
- SOD (superoxide dismutase)
- Catalase
- Glutathione activity
Oxidative stress biomarkers are elevated in both MDD and bipolar disorder.
3. Neurotransmitter Regulation
Curcumin influences:
- Serotonin (5‑HT)
- Dopamine
- Norepinephrine
This supports antidepressant synergy rather than replacement.
4. Increases BDNF (Brain‑Derived Neurotrophic Factor)
BDNF is critical for:
- Neuroplasticity
- Mood regulation
- Memory resilience
Low BDNF is consistently observed in depression.
Curcumin is shown to upregulate BDNF signaling pathways.
5. Gut–Brain Axis Effects
Curcumin improves:
- Gut barrier integrity
- Dysbiosis modulation
- Reduced endotoxin‑triggered neuroinflammation
This is relevant in chronic anxiety + metabolic depression phenotypes.
Why Liposomal Curcumin Is Key
Standard curcumin has extremely poor absorption due to:
- Low solubility
- Rapid metabolism
- Minimal CNS penetration
Liposomal or micellar curcumin provides:
✅ Higher systemic exposure
✅ Better brain inflammatory modulation
✅ Lower dose requirement
✅ Clinically meaningful plasma levels
This is why formulations like Cucimax are increasingly integrated in functional psychiatry support.
Key Published Evidence Titles
“Curcumin as an Adjunctive Treatment for Major Depressive Disorder: A Meta‑Analysis of Clinical Trials”
“Inflammatory Cytokines in Depression and the Role of Curcumin”
“Curcumin Modulates BDNF and Neuroplasticity in Mood Disorders”
“Oxidative Stress Pathways in Bipolar Disorder and Nutraceutical Intervention”
Clinical Summary
| Condition | Key Mechanism | Liposomal Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Parkinson’s/Alzheimer’s | Mitochondrial failure + ROS | Liposomal CoQ10 improves mitochondrial delivery |
| Depression (MDD) | Neuroinflammation + low BDNF | Liposomal curcumin enhances anti-inflammatory action |
| Bipolar Disorder | Oxidative overload + cytokine surges | Better absorption for mood stability support |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Stress, screens, obesity, pollution, and poor lifestyle rhythms are major drivers.
Chronic immune activation in the brain linked to fatigue, mood disorders, and aging.
Yes, oxidative injury disrupts neurotransmitter balance and circadian pathways.
Yes, they enhance cellular delivery and reduce variability.
No, melatonin is also a strong neuroprotective antioxidant.
Better predictability, lower dose, sustained action.
It improves relaxation and calming neurotransmitters like GABA.
Both deficiencies worsen stress resilience and sleep quality.
Yes, through anti‑inflammatory pathways.
It is liposomal/micellar, improving absorption significantly.
It supports mitochondrial energy and reduces oxidative decline.
Improves mitochondrial performance and stamina.
Master antioxidant for stress recovery and longevity.
Yes, oxidative support can aid post‑viral cognitive fatigue.
Yes, under quality formulation and clinical guidance.
No, they complement therapy.
Pregnant women, psychiatric illness patients, chronic disease patients.
Sleep support in weeks, neuroinflammation improvement in 2–3 months.
No, formulation stability matters.
Growing evidence suggests increasing clinical adoption.