Introduction: Why “Unexplained Fatigue” is the Fastest Rising Modern Health Complaint
Across India and globally, one symptom is now becoming almost universal:
- Persistent fatigue
- Low stamina
- Brain fog
- Muscle weakness
- Poor recovery after illness
- Accelerated aging sensations
Yet, many patients are repeatedly told:
- “Your tests are normal.”
- “It’s just stress.”
- “It’s lifestyle.”
Modern functional medicine now recognizes that a common biological root is often overlooked: Mitochondrial dysfunction — the energy crisis inside our cells.
This is why the concept of mitochondrial fatigue has become a major emerging theme in preventive medicine, longevity science, cardiometabolic care, and neuro-aging support.
What Are Mitochondria? The Body’s Cellular Power Plants
Mitochondria are microscopic structures inside every cell.
They are responsible for producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the body’s energy currency.
Every heartbeat, brain signal, muscle movement, immune response, and detoxification pathway depends on:
✅ Healthy mitochondrial output
The organs with highest mitochondrial demand are:
- Brain
- Heart
- Skeletal muscle
- Liver
- Kidneys
When mitochondria decline, fatigue becomes systemic.
Mitochondrial Functions Beyond Energy
Mitochondria are not just energy generators.
They also regulate:
- Oxidative stress balance
- Cellular aging pathways
- Inflammation signaling
- Immune defense
- Neurotransmitter stability
- Apoptosis (cell survival vs cell death)
Thus, mitochondrial aging directly accelerates chronic disease.
What is Mitochondrial Aging?
Mitochondrial aging refers to:
- Reduced ATP production
- Increased ROS (reactive oxygen species)
- Declining membrane integrity
- Inflammatory mitochondrial signaling
- Impaired cellular repair
This leads to what clinicians call:
“Energy-deficient accelerated aging.”
Who Gets Affected the Most? High-Risk Populations
Mitochondrial fatigue is common in:
Metabolic Syndrome & Diabetes
Hyperglycemia drives oxidative mitochondrial damage.
Statin Users
Statins reduce endogenous CoQ10 synthesis.
Chronic Stress and Burnout
Cortisol overload impairs mitochondrial repair.
Neurodegenerative Risk Patients
Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s share mitochondrial failure.
Post-Viral Fatigue (Long COVID)
Persistent mitochondrial inflammation is well documented.
Elderly Individuals
Natural mitochondrial decline is a hallmark of aging.
Symptoms of Mitochondrial Dysfunction (Often Misdiagnosed)
Common symptoms include:
- Chronic fatigue not improved by sleep
- Brain fog
- Poor exercise tolerance
- Muscle weakness
- Low motivation or mood decline
- Sleep disturbance
- Slow recovery after illness
- Accelerated aging perception
Why it is misdiagnosed:
Mitochondrial decline is rarely screened directly, so patients are treated symptomatically without root correction.
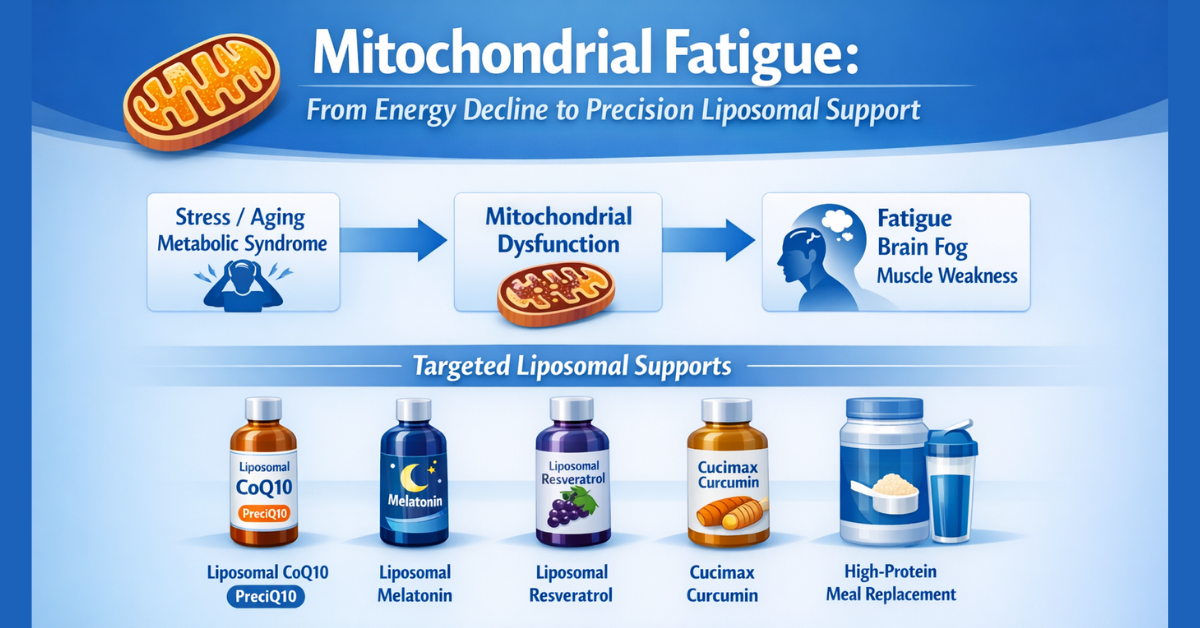
Common Tests vs Special Mitochondrial Assessment Tools
Clinical Tests in Suspected Mitochondrial Fatigue
| Category | Common Tests | Special / Functional Tests (Supervised) |
|---|---|---|
| Metabolic | HbA1c, Lipids | Insulin resistance markers |
| Inflammation | CRP | hs‑CRP, Cytokine panels |
| Nutrient Deficiency | Vitamin D, B12 | CoQ10 levels (specialized) |
| Oxidative Stress | Routine labs normal | Oxidative stress biomarkers |
| Mitochondrial Output | Not measured routinely | Lactate/pyruvate ratios (rare cases) |
Preventing Mitochondrial Aging Naturally
Lifestyle Interventions (Most Evidence-Based)
Exercise (Most Powerful Mitochondrial Stimulus)
Resistance + aerobic exercise increases mitochondrial biogenesis.
Sleep and Circadian Repair
Melatonin regulation supports mitochondrial renewal.
Calorie Restriction / Protein Forward Nutrition
Controlled nutrition reduces metabolic oxidative burden.
Anti-aging Foods
- Polyphenols (berries, turmeric)
- Omega‑3
- Mediterranean-style diet
Role of Supplements in Mitochondrial Fatigue
Supplements help most when:
- Deficiency exists
- Oxidative stress is elevated
- Aging or statin therapy reduces endogenous production
Key mitochondrial actives include:
- CoQ10
- Melatonin
- Resveratrol
- Curcumin
- Glutathione
- Magnesium + Vitamin D3
But the major clinical barrier is:
Poor absorption of many mitochondrial nutraceuticals.
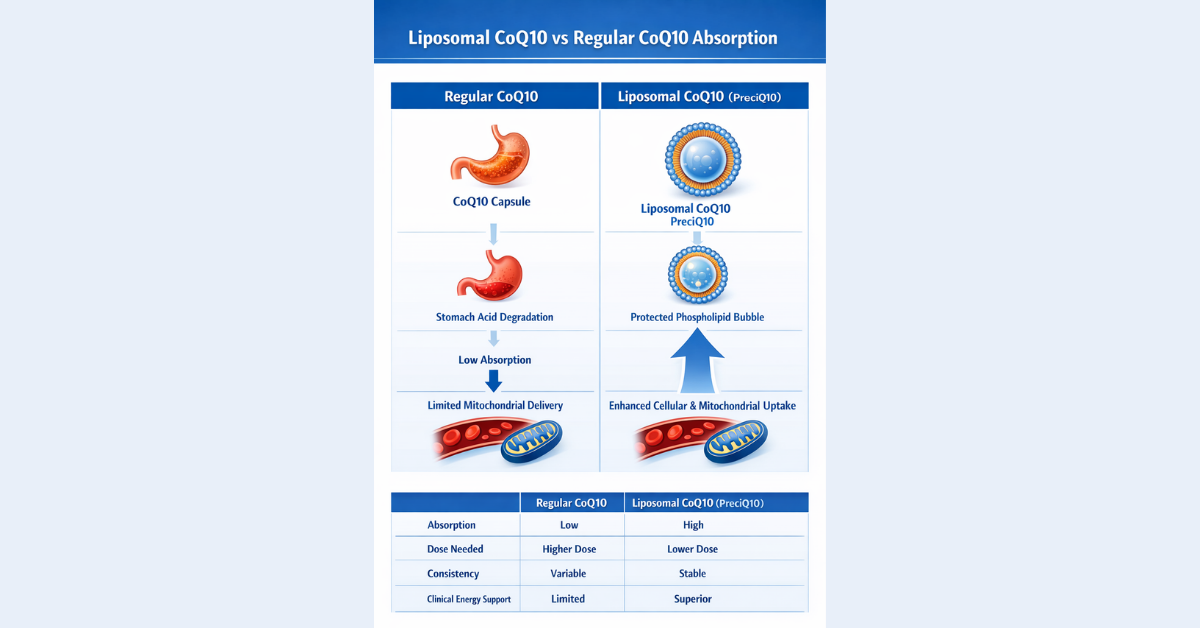
Liposomal CoQ10: Why Delivery Science Matters
Why CoQ10 is Essential
CoQ10 supports:
- Electron transport chain activity
- ATP production
- Neuronal and cardiac mitochondrial stability
CoQ10 depletion is seen in:
- Aging
- Diabetes
- Heart failure
- Statin use
Normal CoQ10 vs Liposomal CoQ10
| Feature | Regular CoQ10 Capsules | Liposomal CoQ10 (PreciQ10) |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption | Low, inconsistent | High, predictable |
| Dose Needed | Higher | Lower effective dose |
| Tissue Delivery | Limited | Enhanced cellular uptake |
| Clinical Impact | Variable fatigue response | Better mitochondrial support |
PreciQ10 provides evidence-aligned CoQ10 delivery for fatigue and aging protocols.
Liposomal Melatonin: Beyond Sleep to Mitochondrial Repair
Melatonin is now recognized as:
- A powerful mitochondrial antioxidant
- Neuroprotective agent
- Circadian regulator
Normal vs Liposomal Melatonin
| Feature | Regular Melatonin | Liposomal Melatonin |
|---|---|---|
| Action | Short-lived | Sustained + predictable |
| Brain antioxidant effect | Limited | Enhanced delivery potential |
| Best use | Occasional insomnia | Neuro-aging + mitochondrial reset |
Liposomal Resveratrol: Longevity and Mitochondrial Signaling
Resveratrol supports:
- SIRT pathways
- Endothelial aging
- Mitochondrial biogenesis
Liposomal formulations improve persistence and clinical reliability.
Liposomal Curcumin (Cucimax): Inflammation and Mitochondrial Stress
Curcumin reduces:
- NF‑κB inflammation
- Oxidative stress mediators
- Neuroinflammatory cascades
Cucimax provides improved absorption compared with standard curcumin.
Literature Evidence After 2020
| Nutraceutical | Evidence Area | Published Focus |
|---|---|---|
| CoQ10 | Parkinson’s, fatigue, cardiac energy | Mitochondrial bioenergetics support |
| Melatonin | Neuroinflammation, aging brain | Mitochondrial antioxidant protection |
| Resveratrol | Longevity pathways | Sirtuins + vascular aging modulation |
| Curcumin | Depression + neuroinflammation | Cytokine + oxidative pathway control |
(These themes are supported by multiple reviews and meta‑analyses published after 2020.)
Medical Conditions Where Mitochondrial Aging is Common
High Mitochondrial Dysfunction Burden
| Condition | Mitochondrial Link |
|---|---|
| Diabetes complications | Oxidative ATP failure |
| Statin-related fatigue | CoQ10 depletion |
| Parkinson’s disease | Complex I dysfunction |
| Alzheimer’s disease | Neuroinflammation + ROS |
| Chronic fatigue syndromes | Energy metabolism collapse |
| Heart failure | Cardiac mitochondrial decline |
| Long COVID | Persistent mitochondrial stress |
Meal Replacement + Calorie Restriction as Mitochondrial Strategy
Calorie restriction is one of the strongest longevity interventions.
Replacing excess carbs with structured high-protein nutrition supports:
- Reduced metabolic oxidative overload
- Better fat loss quality
- Improved mitochondrial efficiency
Precimax meal replacements like Maxlite fit into metabolic mitochondrial recovery frameworks.
Monitoring Supplement Response
If liposomal mitochondrial supplements are started, monitor:
- Fatigue scores
- Exercise tolerance
- Sleep quality
- hs‑CRP (inflammatory status)
- Vitamin D and magnesium correction
- Metabolic markers (HbA1c, lipids)
Duration: typically 8–16 weeks, reassessed clinically.

Who Requires Specialist Assistance?
Doctor supervision is advised for:
- Severe chronic fatigue with unclear diagnosis
- Neurodegenerative disorders
- Patients on anticoagulants (curcumin interaction caution)
- Pregnancy
- Chronic liver or kidney disease
- Multi-drug cardiovascular patients
Conclusion: Mitochondrial Support is the Next Era of Preventive Medicine
Fatigue is not always psychological or lifestyle-driven.
For many individuals, it reflects mitochondrial aging, oxidative stress, and metabolic inflammation.
Liposomal formulations such as:
- PreciQ10 (Liposomal CoQ10)
- Liposomal Melatonin
- Liposomal Resveratrol
- Cucimax (Curcumin)
represent the next frontier of evidence-based mitochondrial care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Energy decline due to mitochondrial dysfunction.
Stress, metabolic syndrome, inflammation, aging.
Diabetics, elderly, statin users, post-viral patients.
Yes, through lifestyle + targeted support.
Essential for ATP and antioxidant defense.
Higher absorption and cellular uptake.
Mitochondrial fatigue, cardiac and brain energy support.
No, it is a mitochondrial antioxidant.
Sustained neuroprotective delivery.
Yes, via inflammation control.
Higher bioavailability.
Yes, through mitochondrial signaling pathways.
No, formulation matters.
Indirect markers + specialized functional tests.
8–16 weeks, then reassess.
No, they complement therapy.
Neurodegeneration, chronic illness, polypharmacy patients.
Yes, improves metabolic efficiency.
Yes, when quality-controlled.
Strong evidence suggests yes.