PreciQ: The Mitochondrial Powerhouse for Optimal Health
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a growing global concern, affecting men and women equally. Increasing stress levels, continuous exposure to pollution, and poor nutrition impact certain organs and cell types more severely, particularly sperms, eggs, the heart, and skeletal muscles, crippling lives. Though Coenzyme Q10 has been known and used for several years, its poor bioavailability as a fat-soluble nutrient has limited the effectiveness of many conventional formulations.
Thanks to modern technologies like micellar, liposomal delivery, and CoQ10 in ubiquinol form, medical science has been able to rediscover the true potential of this critical enzyme. PreciQ represents the next generation of highly bioavailable CoQ10, developed to overcome these limitations and deliver superior results.
Recommended use:
- Male Fertility: Improves sperm quality and function
- Female Fertility: Enhances the quality of eggs produced
- Muscle Pain and Weakness: Beneficial for those experiencing muscle pain and weakness while on statins (atorvastatin, rosuvastatin)
- Heart Care: Dysfunction: Alleviates poor energy and endurance associated with heart dysfunctions.
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Provides relief from symptoms
- Fibromyalgia: Helps manage and reduce symptoms
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Supports neurological health and slows disease progression
- Diabetes and Its Complications: Aids in managing diabetes and reducing related complications
Recommended Dosage: 1 -2 capsules daily, taken with breakfast or lunch, or as recommended by healthcare experts
Best absorbed Coenzyme Q10 -PRECIQ
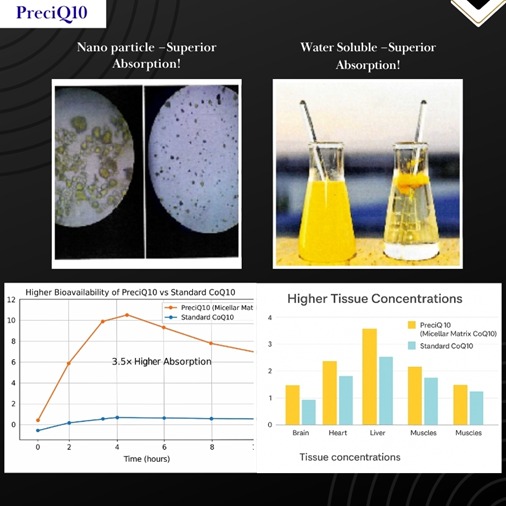
Evidences
Latest Scientific Studies on PreciQ (Highly bioavailable CoQ 10)
Bioavailability of Coenzyme Q10: An Overview of the Absorption Process and Subsequent Metabolism; Jr of Antioxidants 2020
Key findings
The process of CoQ10 absorption is complex. It is not surprising that the absorption and bioavailability of CoQ10 supplements can vary widely and does indeed do so. This variability depends primarily on the formulation of the preparation. As there is considerable inter-individual variability in the uptake of CoQ10, the absorption and bioavailability of CoQ10 also depends on the capacity of a person to absorb a preparation with a given formulation. the importance of CoQ10 crystal dispersion in the initial formulation is emphasised, the absence of which reduces bioavailability by 75%.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7278738/
Coenzyme Q10: Novel Formulations and Medical Trends; Int Jr of Mol.Sci. 2020
Key findings
Great interest in the medical field. Traditionally, CoQ10 clinical use was based on its antioxidant properties; however, a wide range of highly interesting alternative functions have recently been discovered. In this line, CoQ10 has shown pain-alleviating properties in fibromyalgia patients, a membrane-stabilizing function, immune system enhancing ability, or a fundamental role for insulin sensitivity, apart from potentially beneficial properties for familial hypercholesterolemia patients. In brief, it shows a remarkable amount of functions in addition to those yet to be discovered. Despite its multiple therapeutic applications, CoQ10 is not commonly prescribed as a drug because of its low oral bioavailability, which compromises its efficacy. Hence, several formulations have been developed to face such inconvenience. These were initially designed as lipid nanoparticles for CoQ10 encapsulation and distribution through biological membranes and eventually evolved towards chemical modifications of the molecule to decrease its hydrophobicity.
To read more
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/22/8432
Bioavailability Enhancement of Coenzyme Q10: An Extensive Review of Patents: Jr of Drug delivery & Patents 2010
Key findings
Deficiency of this in body leads to several potential disorders like dysfunctions in cellular energetics, neurological degeneration, higher oxidative stress induced damage, breast cancer etc. The high molecular weight and lipophilicity of CoQ10 makes it poorly water soluble and consequently leads to low systemic availability. Several advancements have been made to enhance the bioavailability of CoQ10 using various approaches like size reduction, solubility enhancement (by solid dispersion, prodrug, complexation, ionization) and use of novel drug carriers such as liposomes, microspheres, nanoparticles, nanoemulsions and self-emulsifying system.
To read more
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/46412594_Bioavailability_Enhancement_of_Coenzyme_Q10_An_Extensive_Review_of_Patents
Ubisol-Q10, a Nanomicellar and Water-Dispersible Formulation of Coenzyme-Q10 as a Potential Treatment for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease; Jr of Antioxidants 2021
Key findings
A nanomicellar, water-dispersible formulation of coenzyme-Q10, Ubisol-Q10, has been developed by combining coenzyme-Q10 with an amphiphilic, self-emulsifying molecule of polyoxyethanyl α-tocopheryl sebacate (derivatized vitamin E). This discovery made possible, for the first time, a proper assessment of the true therapeutic value of coenzyme-Q10. Micromolar concentrations of Ubisol-Q10 show unprecedented neuroprotection against neurotoxin exposure in in vitro and in vivo models of neurodegeneration and was extremely effective when delivered either prior to, at the time of, and most significantly, post-neurotoxin exposure. These findings indicate a possible way forward for clinical development due to effective doses well within Federal Drug Administration guidelines. Ubisol-Q10 is a potent mobilizer of astroglia, antioxidant, senescence preventer, autophagy activator, anti-inflammatory, and mitochondrial stabilizer.
To read more
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/46412594_Bioavailability_Enhancement_of_Coenzyme_Q10_An_Extensive_Review_of_Patents
Non-Enzymatic Antioxidants against Alzheimer’s Disease: Prevention, Diagnosis and Therapy; Jr of antioxidants 2023
Key findings
Traditional formulations such as coenzyme Q10 are promising for AD therapy, and they enhance cognition through neuroprotective and antioxidant activities, stabilizing mitochondrial functions and reducing Aβ plaques [8]. Alpha-lipoic acid supplementation is beneficial against AD and acts as an enzymatic cofactor in the regulation of energy production and metabolism, as well as mitochondrial performance. …
To read more
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/46412594_Bioavailability_Enhancement_of_Coenzyme_Q10_An_Extensive_Review_of_Patents
Efficacy of coenzyme Q10 supplementation for male infertility with high sperm DNA fragmentation index: a protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis; BMJ open jr 2022
Key findings
It is well known that normal embryonic development depends on the integrity of complete genetic material from both sperm and oocytes.1 Among the factors that influence the normal development of embryos and fetuses, the integrity of sperm DNA is important.2 Multiple studies have demonstrated that sperm DNA integrity plays a crucial role in embryo development3–5 and has the capacity to predict the final pregnancy outcome.6 However, the current evaluation of infertile men commonly relies on semen analysis, which still has a limitation of inaccuracy in predicting male fertility potential and final pregnancy outcome from assisted reproductive technology (ART).7 The Sperm DNA Fragmentation Index (SDFI), as an indicator reflecting sperm DNA integrity, can offset this limitation. The antioxidant effect of CoQ10 manifests as preventing membrane phospholipid peroxidation and free radical oxidation.16 Given its excellent antioxidation, CoQ10 supplementation has been applied for decades to improve semen parameters with good clinical efficacy.1
To read more
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10254600/
Does coenzyme Q10 supplementation improve fertility outcomes in women undergoing assisted reproductive technology procedures? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials; Jr of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics 2020
Key findings
Oral supplementation of CoQ10 resulted in an increase of CPR when compared with placebo or no-treatment (28.8% vs. 14.1%, respectively; OR 2.44, 95% CI 1.30–4.59, p = 0.006; I2 32%). This effect remained significant when women with poor ovarian response and polycystic ovarian syndrome were analyzed separately. Oral supplementation of CoQ10 may increase CPR when compared with placebo or no-treatment, in women with infertility undergoing ART procedures,
To read more
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10815-020-01906-3
Coenzyme Q10 and Male Infertility: A Systematic Review; Jr of Antioxidants 2022
Key findings
Infertility affects 15% of couples worldwide. A male factor is involved in 50% of cases. The etiology of male infertility is poorly understood, but there is evidence for a strong association between oxidative stress (OS) and poor seminal fluid quality. For this reason, therapy with antioxidants is one of the cornerstones of empirical treatment of male infertility. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)—an essential cofactor for energy production with major antioxidant properties—is commonly used to support spermatogenesis in idiopathic male infertility. This systematic review aims to elucidate the usefulness of CoQ10 supplementation in the treatment of male infertility, particularly with regard to semen quality assessed by conventional and advanced methods, and pregnancy rates. All studies report a beneficial effect of CoQ10 supplementation on semen parameters, although randomized controlled trials are a minority. Moreover, the optimal dosage of CoQ10 or how it can be combined with other antioxidant molecules to maximize its effect is unknown. However, CoQ10 is still one of the most promising molecules to treat idiopathic male infertility and warrants further investigation.
To read more
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/10/6/874
The Effect of CoQ10 supplementation on ART treatment and oocyte quality in older women; Jr of Human Fertility 2023
Key findings
A significant problem associated with assisted reproductive technologies (ART) is recurrent treatment failure which can be attributed to the age-associated decline in oocyte quality. Co-enzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is an antioxidant and essential component of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. It is reported that de novo CoQ10 production declines with ageing and coincides with age-related decline in fertility, leading to CoQ10 supplementation being advocated to enhance response to ovarian stimulation and improve oocyte quality. CoQ10 supplementation was found to improve fertilization rates, embryo maturation rates and embryo quality when used before and during in vitro fertilization (IVF) and in vitro maturation (IVM) treatment in women aged 31 and over. Regarding oocyte quality, CoQ10 was able to reduce high rates of chromosomal abnormalities and oocyte fragmentation, as well as improve mitochondrial function. Proposed mechanisms of CoQ10 function include restoration of reactive oxygen species imbalance, preventing DNA damage and oocyte apoptosis, as well as restoration of Krebs cycle downregulation from ageing. In this literature review, we provide an overview of the use of CoQ10 in improving the success of IVF and IVM in older women, and additionally assess the impact of CoQ10 on oocyte quality and discuss potential mechanisms of action by CoQ10 on the oocyte.
To read more
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37102567/
Coenzyme Q10 Stimulate Reproductive Vatality: Drug Design Dev Therapy 2023
Key findings
Female infertility and pregnancy maintenance are associate with various factors, including quantity and quality of oocytes, genital inflammation, endometriosis, and other diseases. Women are even diagnosed as unexplained infertility or unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion when failed to achieve pregnancy with current treatment, which are urgent clinical issues need to be addressed. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a lipid-soluble electron carrier in the mitochondrial electron transport chain. It is not only essential for the mitochondria to produce energy, but also function as an antioxidant to maintain redox homeostasis in the body. Recently, the capacity of CoQ10 to reduce oxidative stress (OS), enhance mitochondrial activity, regulate gene expression and inhibit inflammatory responses, has been discovered as a novel adjuvant in male reproductive performance enhancing in both animal and human studies. Furthermore, CoQ10 is also proved to regulate immune balance, antioxidant, promote glucose and lipid metabolism. These properties will bring highlight for ovarian dysfunction reversing, ovulation ameliorating, oocyte maturation/fertilization promoting, and embryonic development optimizing. In this review, we systematically discuss the pleiotropic effects of CoQ10 in female reproductive disorders to investigate the mechanism and therapeutic potential to provide a reference in subsequent studies.
To read more
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10475284/
Beneficial antioxidant effects of Coenzyme Q10 on reproduction: Jr of Vit Hormones 2023
Key findings
General aspects of CoQ10, such as its role as an antioxidant and in mitochondrial bioenergetics are considered. The age-dependent decline in human female reproductive potential is associated with cellular mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, and in some cases accompanied by a decrease in CoQ10 levels. Herein, we discuss experimental and clinical evidence on CoQ10 protective effects on reproductive health. We also address the potential of supplementation with this coenzyme to rescue reprotoxicity induced by exposure to environmental xenobiotics. The use of CoQ10 supplementation can improve reproductive performance through the scavenging of reactive oxygen species and free radicals. This strategy can constitute a low-risk and low-cost strategy to attenuate the impact on fertility related to aging and exposure to environmental chemicals.
To read more
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36707133/
Antioxidant CoQ10 Restores Fertility by Rescuing Bisphenol A-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage in the Caenorhabditis elegans Germline; Genetics 2020
Key findings
Supplementation with the antioxidant Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) rescues the reprotoxicity induced by the widely used plasticizer and endocrine disruptor bisphenol A (BPA), in part by neutralizing DNA damage resulting from oxidative stress. CoQ10 significantly reduces BPA-induced elevated levels of germ cell apoptosis, phosphorylated checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK-1), double-strand breaks (DSBs), and chromosome defects in diakinesis oocytes. BPA-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and increased gene expression of antioxidant enzymes in the germline are counteracted by CoQ10. Finally, CoQ10 treatment also reduced the levels of aneuploid embryos and BPA-induced defects observed in early embryonic divisions. We propose that CoQ10 may counteract BPA-induced reprotoxicity through the scavenging of reactive oxygen species and free radicals, and that this natural antioxidant could constitute a low-risk and low-cost strategy to attenuate the impact on fertility by BPA.
To read more
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31852725/
Targeted Treatment of Age-Related Fibromyalgia with Supplemental Coenzyme Q10; Jr of Advanced Biomedicals 2021
Key findings
Fibromyalgia is a common chronic pain condition of unknown aetiology, although mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation have been implicated in the pathophysiology of this disorder. Treatment generally involves physiotherapy, anticonvulsants, and antidepressant therapy; however, the symptomatic relief conferred by these treatments can be very variable, and there is a need for additional therapeutic strategies. One such treatment which is gaining a lot of interest is the use of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) supplementation. The therapeutic efficacy associated with CoQ10 supplementation is thought to arise from the ability of supplementation to restore an underlying deficit in CoQ10 status which has been associated with fibromyalgia together with the ability of CoQ10 to improve mitochondrial activity, restore cellular antioxidant capacity, and ameliorate inflammation.
To read more
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33725346/
Coenzyme Q10 supplementation alleviates pain in pregabalin-treated fibromyalgia patients via reducing brain activity and mitochondrial dysfunction: Jr of Free Radicals Res 2019
Key findings
Pregabalin alone reduced pain and anxiety via decreasing brain activity compared with their baseline. However, it did not affect mitochondrial oxidative stress and inflammation. Supplementation with CoQ10 effectively reduced greater pain, anxiety and brain activity, mitochondrial oxidative stress, and inflammation. CoQ10 also increased a reduced glutathione levels and superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels in FM patients. These findings provide new evidence that CoQ10 supplementation provides further benefit for relieving pain sensation in pregabalin-treated FM patients, possibly via improving mitochondrial function, reducing inflammation, and decreasing brain activity.
To read more
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31387429/
Supplementation of maturation medium with CoQ10 enhances developmental competence of ovine oocytes through improvement of mitochondrial function; Jr of Molecular Develop 2019
Key findings
In conclusion, supplementation with CoQ10 improves the quality of COCs and the subsequent developmental competence of the embryo.
To read more
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31066163/
Obesity-induced oocyte mitochondrial defects are partially prevented and rescued by supplementation with co-enzyme Q10 in a mouse model; Jr Human Reproduction 2016
Key findings
CoQ10 supplementation significantly increased the levels of metabolites and decreased ROS levels in oocytes from normal diet mice but not in oocytes from HF/HS mice. However, CoQ10 completely prevented the mitochondrial distribution abnormalities observed in the HF/HS mice. Overall, CoQ10 supplementation significantly increased the percentage of normal spindle and chromosome alignment (92.3 versus 80.2%, P= 0.039). In the sub-analysis by diet, the difference did not reach statistical significance. When undergoing IVF, there were no statistically significant differences in the number of mature oocytes, the fertilization rate, blastocyst formation rates, implantation rates, resorption rates or litter size between HF/HS mice receiving CoQ10 or vehicle injections.
To read more
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27432748/
Coenzyme Q10, oxidative stress, and male infertility: A review; Jr of Reproductive Health 2021
Key findings
Male infertility has a complex etiopathology, which mostly remains elusive. Although research has claimed that oxidative stress (OS) is the most likely underlying mechanism of idiopathic male infertility, the specific treatment of OS-mediated male infertility requires further investigation. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), a vitamin-like substance, has been found in measurable levels in human semen. It exhibits essential metabolic and antioxidant functions, as well as playing a vital role in mitochondrial bioenergetics. Thus, CoQ10 may be a key player in the maintenance of biological redox balance. CoQ10 concentrations in seminal plasma directly correlate with semen parameters, especially sperm count and sperm motility. Seminal CoQ10 concentrations have been shown to be altered in various male infertility states, such as varicocele, asthenozoospermia, and medical or surgical regimens used to treat male infertility. These observations imply that CoQ10 plays an important physiological role in the maintenance and amelioration of semen quality.
To read more
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34078005/
CoQ10 Treatment to Improve Fertility in Elderly Patients; Clinical trials registrar 2023
Key findings
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a vitamin-like antioxidant, essential for proper function of mitochondrial respiratory chain. It has been shown that there is a decrease level of CoQ10 in several tissues with aging (like muscle). We suggest that one possible explanation for altered oocyte mitochondrial function may be diminished CoQ10 substrate availability or utilization as a function of aging. The oocytes, and in fact the pre-granulosa cells which give rise to the granulosa (GC) and cumulus cells (CC), are unique in the body since there is no cell division for many years. Therefore, in older women, the oocytes and GCs in primordial follicles will have been exposed to low levels of radical oxygen species produced by mitochondrial respiration over decades, resulting in possible cumulative damage to mitochondria and DNA. Decreased availability of CoQ10 would contribute to reduced antioxidant activity and decreased ATP production by the mitochondria in the oocyte. In addition, compromised mitochondrial function in GCs can effect steroid hormone production, as steroidogenesis is initiated in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Thus, a vicious circle is created by which decreased CoQ10 bioavailability with advanced age could adversely affect meiosis and further developmental competence of gametes.
To read more
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02010164





Tarang Jain –
I was using water soluble CoQ 10 regularly and did not get it in india, till i find PreciQ 10. Right product for those who are looking for highly absorbable CoQ 10.
radharam –
i have used PreciQ to improve my egg quality along with clomiphene and it was very effective. For ladies seeking fertility in their 30’s preciq can be a good choice.
Mudhraj –
My statin related muscle pain/weakness reduced very fast within 3 weeks and i am happy with prreciQ
Aamir Hussain –
My doctor suggested taking good quality Coenzyme Q10 for improving my sperm quality and therafter i started taking PreciQ.
after 3 months at 100mg twice daily my sperm quality has improved appreciably.