Introduction
Creatine is often misunderstood as a supplement meant only for male athletes or bodybuilders. Modern science tells a very different story. Creatine is a naturally occurring compound made in the body and obtained from food, playing a critical role in energy production in muscles and the brain. Emerging research shows that women—across life stages and activity levels—can benefit significantly from creatine supplementation, not just for fitness, but also for recovery, bone health, cognition, and overall vitality.
This article explores the current scientific evidence on creatine supplementation in women, who can benefit most, what to expect, types and dosing, and why innovative formats like fast‑acting effervescent creatine granules (Precimax Creatine) are changing how creatine is used.

What Is Creatine and Why It Matters for Women
Creatine helps regenerate ATP, the body’s immediate energy currency. About 95% of creatine is stored in skeletal muscles, with the rest supporting brain and cellular energy needs.
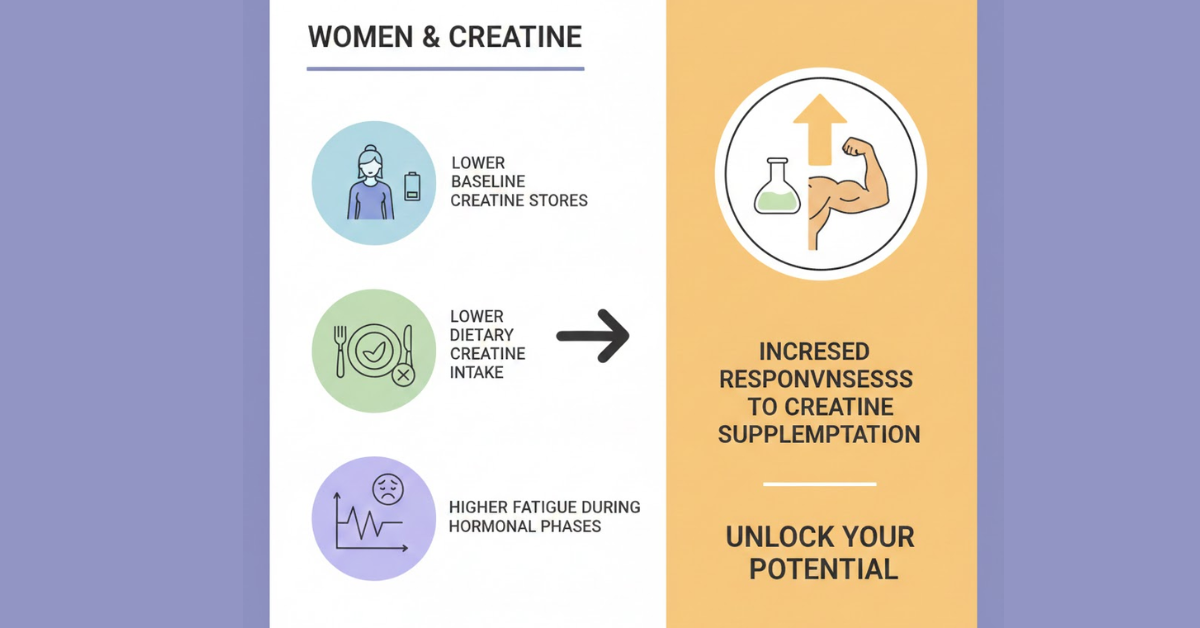
Women generally have:
- Lower baseline creatine stores than men
- Lower dietary creatine intake
- Higher fatigue susceptibility during certain hormonal phases
This makes women especially responsive to creatine supplementation.
Why Creatine Supplementation Is Beneficial for Women
1. Improves Strength and Lean Muscle – Creatine supports strength gains and lean muscle development without masculinizing effects. For women, this translates to better functional strength, metabolism, and body composition.
2. Enhances Recovery and Reduces Fatigue – Creatine helps reduce muscle soreness and improves recovery—particularly useful for busy women balancing work, home, and fitness.
3. Supports Bone and Joint Health – When combined with resistance training, creatine may support bone density—important during perimenopause and post‑menopause.
4. Cognitive and Mental Energy Support – Creatine supports brain energy metabolism, improving mental clarity, focus, and resistance to mental fatigue.
5. Menstrual and Hormonal Phase Support – Studies suggest creatine may reduce fatigue during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
Who Should Consider Creatine?
- Active women and gym‑goers
- Women with low muscle mass or fatigue
- Vegetarians and vegans
- Perimenopausal and postmenopausal women
- Women recovering from illness or injury
- Women with high cognitive or physical demands
What to Expect After Starting Creatine
- Improved workout performance within 7–14 days
- Better recovery and reduced soreness
- Mild water retention initially (intracellular, not bloating)
- Gradual improvements in strength, endurance, and energy
Types of Creatine Supplementation
Creatine Monohydrate
- Most researched and effective form
- High bioavailability
- Gold standard for supplementation
Other Forms (Citrate, Ethyl Ester, Chelates)
- Limited evidence of superiority
- Often more expensive without added benefit
Conclusion: Creatine monohydrate remains the preferred form based on science.
Dose, Duration, and How to Take It
Recommended Dose for Women
- 3–5 g per day
- No loading phase required
Duration
- Can be taken continuously for months
- Periodic breaks are optional
Timing
- Anytime during the day
- Post‑workout preferred if training
Why Innovative Forms Like Precimax Creatine Granules Matter
Traditional creatine powders may have solubility and stability issues. Fast‑acting effervescent creatine granules address these challenges.
Benefits of Effervescent Creatine Granules
- Faster absorption due to effervescence
- Better solubility and taste
- Reduced risk of creatinine formation
- Gentle on digestion
- Convenient and palatable for daily use
Precimax Creatine Effervescent Granules represent a modern, user‑friendly evolution of creatine supplementation—especially suitable for women new to creatine.
Conditions Where Creatine Can Create a Positive Impact in Women
- Sarcopenia (age‑related muscle loss)
- Chronic fatigue and low energy states
- Recovery after illness or surgery
- Cognitive stress and mental fatigue
- Vegetarian/vegan nutrient gaps
- Perimenopausal muscle and bone decline
Can Creatine Be Combined With Other Agents?
Yes. Creatine works well with:
- Protein or EAAs for muscle support
- Magnesium for energy metabolism
- Vitamin D3 for bone and muscle health
- Omega‑3s for inflammation control

Expert Opinions
Dr. Shanthakumari, Hyderabad
“Creatine is no longer just a sports supplement. In women, it can support muscle health, energy, and recovery—especially during hormonal transitions—when used responsibly.”
Dr. Pradhan Singh, Kolkata
“Evidence supports creatine as a safe and effective supplement for women when taken at recommended doses, even outside athletic settings.”
Mita Singh, Registered Dietitian, Karnal
“For vegetarian women, creatine supplementation can fill an important nutritional gap and support both physical and mental performance.”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is creatine safe for women?
Yes, when used at recommended doses.Will creatine cause weight gain?
It may cause mild water retention inside muscles, not fat gain.Can women take creatine without working out?
Yes, but benefits are greater with physical activity.How long can I take creatine?
It can be taken safely for months; long‑term use is well studied.Do I need a loading phase?
No, 3–5 g daily is sufficient.Is creatine only for athletes?
No, it benefits general health and energy too.Is creatine safe during menstruation?
Yes, and it may reduce fatigue.Can vegetarians take creatine?
Yes, and they may benefit more.Does creatine affect hormones?
No adverse hormonal effects have been shown.Can creatine help with brain fog?
It may support mental energy and focus.Is water retention permanent?
No, it is temporary and intracellular.Should I consult my doctor before taking creatine?
Yes, especially if you have medical conditions.How soon will I see benefits?
Within 1–2 weeks for energy and performance.Is weight training mandatory with creatine?
Not mandatory, but recommended for best results.Can creatine be taken with other supplements?
Yes, it stacks well with protein, magnesium, and vitamin D.Is effervescent creatine better than powder?
It may offer better absorption and ease of use.Do I need a prescription for creatine?
No, but medical guidance is advisable.
Final Takeaway
Creatine is a science‑backed, versatile supplement that can positively impact women’s strength, energy, recovery, and overall health. With innovative formats like Precimax Creatine Effervescent Granules, creatine supplementation is now more accessible, effective, and women‑friendly than ever before.