If you’ve been struggling with stubborn bloating, unpredictable digestion, or fatigue that never seems to go away, there’s a chance your gut might be trying to tell you something deeper. One common but often overlooked cause behind these issues is SIBO—Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. While our gut naturally houses trillions of bacteria, they’re supposed to live mostly in the large intestine. The small intestine, on the other hand, should have only a small number of microbes. When bacteria multiply where they shouldn’t—particularly in the small intestine—they begin to ferment food too early, causing discomfort and disrupting nutrient absorption. That’s SIBO. The good news? With the right support—especially powerful ingredients like lactoferrin, liposomal lactoferrin, advanced probiotics like PRIZIBIOME, and targeted herbal antimicrobials—SIBO can be managed effectively and sustainably. Let’s break down the root problem, how to recognize it, and the latest science-backed solutions that are transforming gut health today.
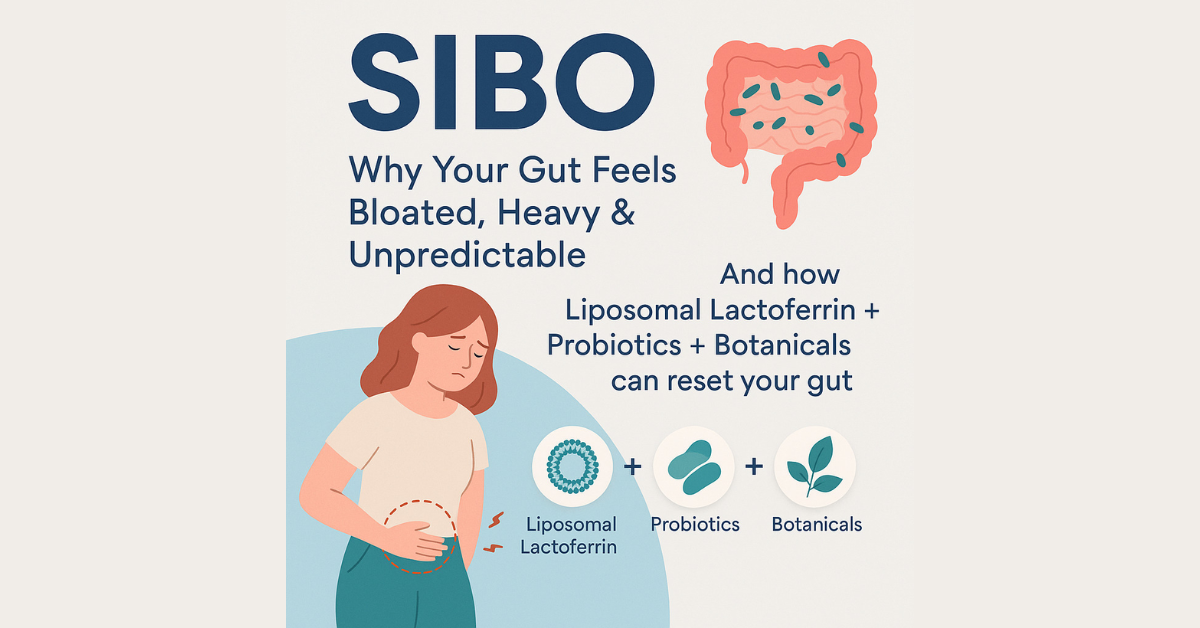
What Exactly is SIBO?
Think of your digestive system as a finely organized neighborhood. Each part has its own residents, and when bacteria move into the wrong area and start overpopulating, chaos begins.
In SIBO:
- Bacteria ferment food too early
- Excess gas is produced (hydrogen, methane, or hydrogen sulfide)
- The intestinal lining becomes inflamed
- Nutrients don’t get properly absorbed
- The immune system becomes irritated and weakened
Over time, this imbalance can lead to widespread health issues beyond digestion—including mood shifts, skin flare-ups, and chronic fatigue.
Symptoms: SIBO Isn’t Just About Gas
SIBO shows up differently in different people. Here are the most common red flags:
- Persistent bloating—especially after meals
- Frequent gas or belching
- Diarrhea, constipation, or switching between both
- Stomach pain or cramping
- Heartburn or indigestion
- Feeling full too quickly
- Weakness or low energy
- Weight fluctuations
- Nutrient deficiencies (like Vitamin B12 and iron)
- Skin issues such as acne or rosacea
Interestingly:
- Hydrogen-based SIBO = diarrhea dominated
- Methane-based SIBO = constipation dominated
- Hydrogen sulfide SIBO = severe pain, foul-smelling gas
Because symptoms overlap with IBS, many people go undiagnosed for years.
What Causes SIBO?
SIBO isn’t random—it usually develops when the gut’s defense and movement mechanisms stop working the way they should. Major triggers include:
- Low stomach acid
Stomach acid kills unwanted bacteria. Low levels? More bacteria survive. - Slow gut motility
When food moves sluggishly, bacteria get more time to multiply. - Structural changes
Surgery, scar tissue, or anatomical issues can trap bacteria. - Chronic inflammation
From food sensitivities, infections, or autoimmune diseases. - Gut microbiome imbalance
Often caused by repeated antibiotic use, stress, or processed food. - Weakened gut immunity
The body struggles to maintain microbial balance. - Poor digestive enzyme or bile flow
Food remains partially digested—perfect for bacterial feeding.
Understanding the cause helps tailor the right recovery approach.
Conventional SIBO Treatment: What Works
Doctors often start with:
Antibiotics
- Rifaximin (best for hydrogen SIBO)
- Rifaximin + Neomycin (for methane SIBO)
- Others depending on severity
Herbal Antimicrobials
Equally effective in many cases:
- Berberine
- Allicin (from garlic)
- Oregano oil
- Neem, grape seed extract
Digestion & Motility Support
- Digestive enzymes
- Bile flow support
- Natural/medical prokinetics
Rebalancing Gut Bacteria
- Probiotics (high-quality and multi-strain)
- Prebiotics in later stages
Dietary Support
- Low-FODMAP diet
- SIBO-specific plans
- Elemental diet for severe cases
But research now highlights a major breakthrough support ingredient for SIBO recovery:
Lactoferrin — The Underestimated Hero for Gut Healing
Lactoferrin is a natural immune protein found in milk and mucosal fluids. It’s gentle, powerful, and uniquely suited for SIBO recovery.
What Makes Lactoferrin So Effective?
- Targets harmful bacteria — protects the good ones
By binding iron (which bacteria need), lactoferrin starves out the bad guys without disrupting friendly microbes. - Breaks down bacterial biofilms
Biofilms are like protective shields that help bacteria survive antibiotics. Lactoferrin breaks them apart—making treatments more successful. - Repairs the gut lining
Reduces inflammation and supports tight junctions, easing leaky gut problems. - Strengthens intestinal immunity
Helps your body maintain bacterial balance naturally. - Reduces die-off reactions
Eases the discomfort many feel during bacterial detox.
Why Liposomal Lactoferrin is a Game Changer?
Traditional lactoferrin can degrade in the stomach. Liposomal technology surrounds it in a protective layer so it:
- Absorbs better
- Reaches deeper into the gut
- Provides stronger anti-inflammatory action
- Is gentler on sensitive digestion
This makes liposomal lactoferrin—like the one being formulated by Precimax Life Sciences—an extremely promising tool in SIBO therapy.
Probiotics & SIBO: Meet PRIZIBIOME — Precision Support for Gut Rebalance
Probiotics alone cannot eradicate SIBO. But they are essential for:
- Preventing harmful bacteria from returning
- Reducing digestive symptoms
- Improving intestinal motility
- Repairing the gut lining
- Supporting immune balance
PRIZIBIOME’s clinically validated strains help:
👉 Rebalance the microbiome without excess gas
👉 Soothe inflammation
👉 Strengthen gut barrier function
👉 Work synergistically with lactoferrin
The right probiotic at the right phase is vital—especially after antimicrobials or antibiotics.
The Right Diet Makes All the Difference
Food is fuel—but also food for bacteria. SIBO healing works best with a phased diet:
Phase 1 — Active Treatment
Goal: Starve excess bacteria
- Low-FODMAP or SIBO-Specific Diet
- Elemental diet only in severe cases
Avoid:
- Wheat
- Beans/lentils
- Onions/garlic
- Apples/pears
- Artificial sweeteners
Choose:
- Eggs, chicken, fish
- Rice, quinoa
- Cooked low-FODMAP veggies
- Berries, citrus fruits
Phase 2 — Healing Transition
Goal: Repair the gut lining
- Bone broth
- Cooked veggies
- Fermented foods (if tolerated)
- Healthy fats like ghee, olive oil
Limit raw foods and high-fiber grains early on.
Phase 3 — Long-Term Maintenance
Goal: Balanced digestion
- Mediterranean-style diet
- Resistant starches (cooked & cooled potato/rice)
- Minimal sugar & processed foods
This is where probiotics + lactoferrin shine to maintain stability.
A Simple SIBO Support Protocol
| Step | Focus | Tools |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reduce overgrowth | Antibiotics or botanicals |
| 2 | Gut protection | Liposomal lactoferrin |
| 3 | Improve motility & digestion | Enzymes + bile support |
| 4 | Restore microbiome | PRIZIBIOME probiotics |
| 5 | Diet phases | Low-FODMAP → Healing → Balanced |
| 6 | Prevent relapse | Lifestyle + ongoing supplements |
Recovery takes commitment, but results are worth it.
Conclusion: SIBO Can Be Managed—Naturally & Effectively
SIBO is more than a temporary digestive upset—it’s a complex imbalance that needs thoughtful care. But recovery is absolutely achievable.
Lactoferrin, especially in liposomal form, stands out for its ability to:
- Target harmful bacteria selectively
- Support powerful but gentle intestinal healing
- Break down biofilms for better treatment results
- Strengthen immunity for long-term balance
- Reduce relapse risk
Added to a protocol with:
✔ Multi-strain probiotics like PRIZIBIOME
✔ Proven botanical antimicrobials
✔ Smart diet transitions
✔ Lifestyle adjustments
you can restore gut harmony, reclaim digestion, and feel energized again. Your gut is incredibly resilient—it just needs the right support to thrive.
FAQs Specifically About Lactoferrin (and Liposomal Lactoferrin)
- How does lactoferrin help in SIBO?
Ans – Lactoferrin reduces harmful bacteria, disrupts biofilms, strengthens intestinal immunity, and repairs the gut lining—making it highly beneficial for SIBO recovery.
- Why is liposomal lactoferrin better than regular lactoferrin?
Ans – Liposomal lactoferrin has superior absorption, better stability, higher bioavailability, and improved gastrointestinal tolerability, making it more effective for gut repair.
- Can lactoferrin replace antibiotics in SIBO treatment?
Ans – Lactoferrin does not replace antibiotics in severe cases but significantly enhances their effectiveness and reduces side effects. It can be used alone in mild-to-moderate cases or as part of a combined strategy.
- Does lactoferrin kill good bacteria?
Ans – No. Lactoferrin selectively inhibits harmful bacteria while supporting beneficial gut flora—making it safer than broad-spectrum antimicrobials.
- Is lactoferrin safe for long-term use?
Ans – Yes. Lactoferrin is naturally present in human milk and safe for daily use. Liposomal forms offer even better tolerability.
- Can lactoferrin help with inflammation caused by SIBO?
Ans – Yes. Lactoferrin reduces inflammatory cytokines and helps heal the intestinal lining, making it useful for both SIBO and post-SIBO recovery.
- Is lactoferrin helpful for constipation-type (methane-dominant) SIBO?
Ans – Yes. By reducing methane-producing archaea and restoring gut motility, lactoferrin benefits both diarrhea- and constipation-dominant SIBO.
- Can lactoferrin help prevent SIBO relapse?
Ans – Absolutely. Its immune-strengthening, anti-inflammatory, and microbiome-supportive actions make lactoferrin ideal for long-term maintenance.
- Can lactoferrin be taken with probiotics?
Ans – Yes. Lactoferrin works synergistically with probiotics, helping healthy strains colonize more effectively.
- Does lactoferrin help reduce die-off reactions?
Ans – Yes. Lactoferrin moderates inflammation and oxidative stress, helping patients tolerate SIBO treatment with fewer discomfort episodes.
FAQs Related to PRIZIBIOME (Multi-Strain Probiotics)
- Can PRIZIBIOME be taken during SIBO treatment?
Ans – In many cases, yes—but timing matters. Some practitioners start probiotics during treatment; others start after the bacterial load reduces. PRIZIBIOME is ideal in the rebalancing and maintenance phases.
- What makes PRIZIBIOME different from regular probiotics?
Ans – PRIZIBIOME contains multi-strain, clinically validated probiotic species that support immunity, gut barrier repair, digestion, and inflammation control—helpful for SIBO recovery.
- Will probiotics worsen my bloating or gas?
Ans – High-FODMAP prebiotics may worsen symptoms, but PRIZIBIOME’s strains are chosen for high tolerance even in sensitive individuals.
- Are probiotics needed after SIBO antibiotics?
Ans – Yes. Antibiotics reduce bacterial overgrowth but also disturb the gut ecosystem. PRIZIBIOME helps restore balance and prevent relapse.
- Can PRIZIBIOME help with post-SIBO constipation or diarrhea?
Ans – Yes. Different strains regulate motility, reduce gas-producing bacteria, and support mucosal repair—helping normalize bowel habits.
General SIBO-Related FAQs
- Why does SIBO keep coming back?
Ans – Because the underlying causes—slow motility, low stomach acid, inflammation, dysbiosis, surgery, diet, or hormonal issues—are not addressed. Maintenance with probiotics, lactoferrin, and diet reduces recurrence.
- What is the best diet during SIBO treatment?
Ans – Low-FODMAP and SIBO-specific diets are most helpful during treatment. Elemental diets are used for severe cases. A Mediterranean-style diet works best for long-term maintenance.
- Can herbal antimicrobials treat SIBO as effectively as antibiotics?
Ans – Yes. Berberine, allicin, oregano oil, and neem have strong evidence. They often work as well as antibiotics, with fewer side effects.
- How long does it take to recover from SIBO?
Ans – Depending on severity, SIBO treatment may last 4–12 weeks, followed by a 3–6 month maintenance phase with lactoferrin + probiotics.
- How do I know if my SIBO is improving?
Ans – Reduced bloating, better bowel movements, improved energy, decreased reflux, and less abdominal pain typically indicate improvement. Breath tests can confirm bacterial reduction.